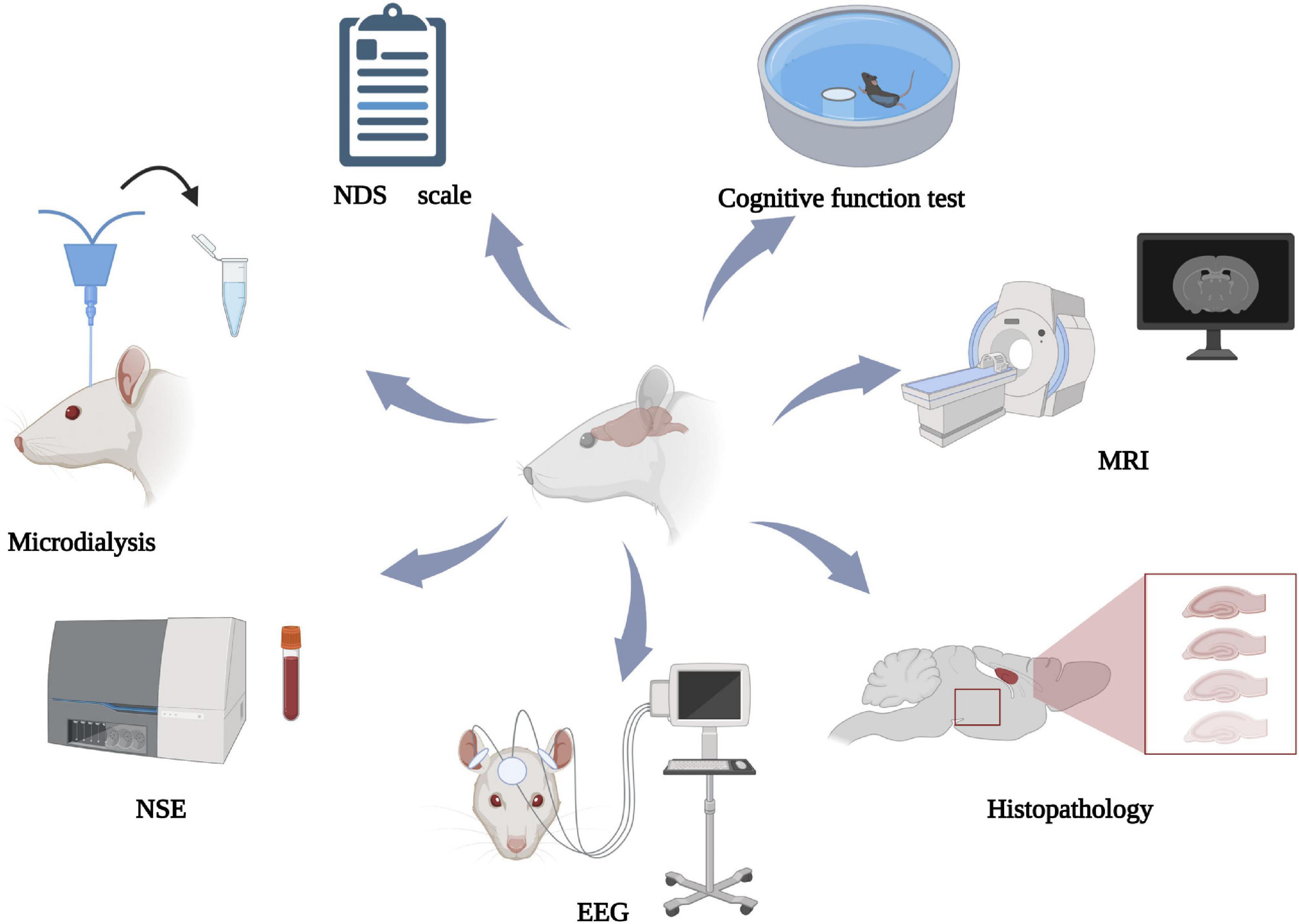
Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest
Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest - The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. There are four key focal areas:. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs.
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. There are four key focal areas:. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially.
Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. There are four key focal areas:.
Cardiac Arrest Induced by Asphyxia Versus Ventricular Fibrillation
Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. There are four key focal areas:. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
There are four key focal areas:. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and.
Development and Evaluation of a Novel Mouse Model of Asphyxial Cardiac
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. There.
Development and Evaluation of a Novel Mouse Model of Asphyxial Cardiac
Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. There.
Cardiac Arrest Induced by Asphyxia Versus Ventricular Fibrillation
Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. There are four key focal areas:. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
There are four key focal areas:. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the.
Development and Evaluation of a Novel Mouse Model of Asphyxial Cardiac
Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. There are four key focal areas:. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
There are four key focal areas:. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the.
Frontiers Rat model of asphyxiainduced cardiac arrest and resuscitation
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. There.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest (ca) refers to the cessation of mechanical activity of the heart and the disappearance of circulatory signs. There are four key focal areas:. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the.
Cardiac Arrest (Ca) Refers To The Cessation Of Mechanical Activity Of The Heart And The Disappearance Of Circulatory Signs.
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Sudden cardiac arrest is a significant source of morbidity and mortality, with neurological injury affecting the majority of persons who initially. There are four key focal areas:.