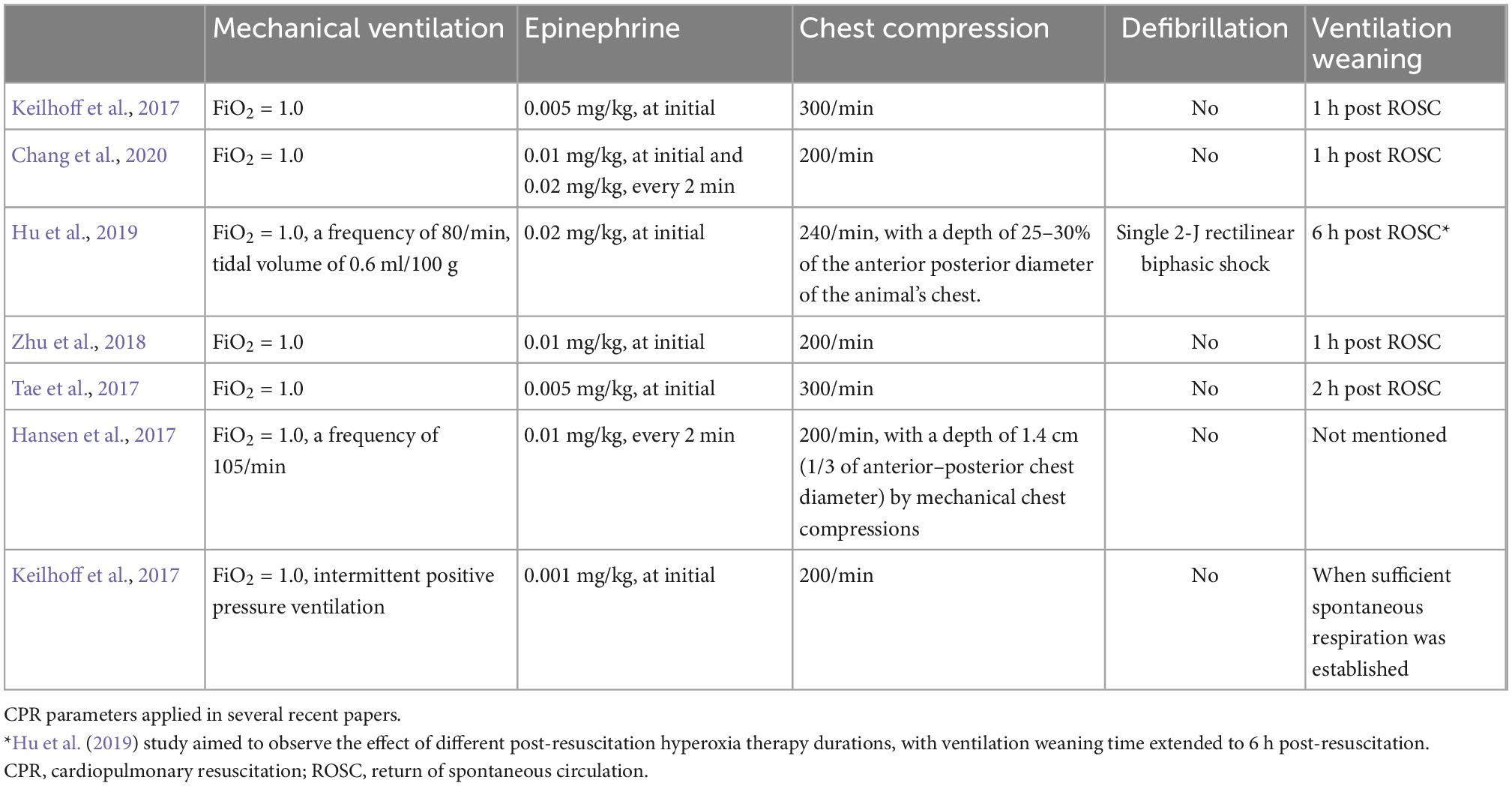
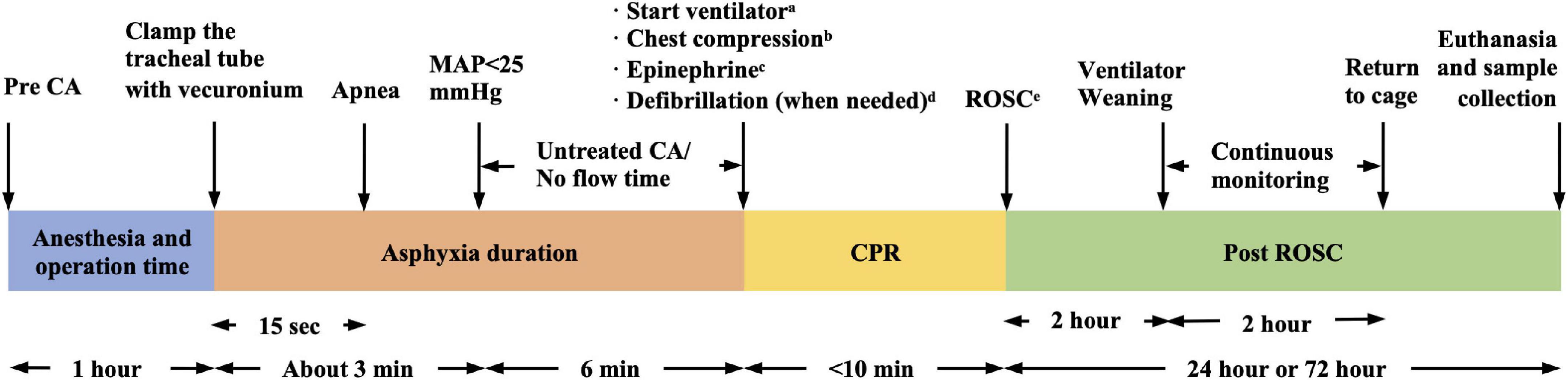
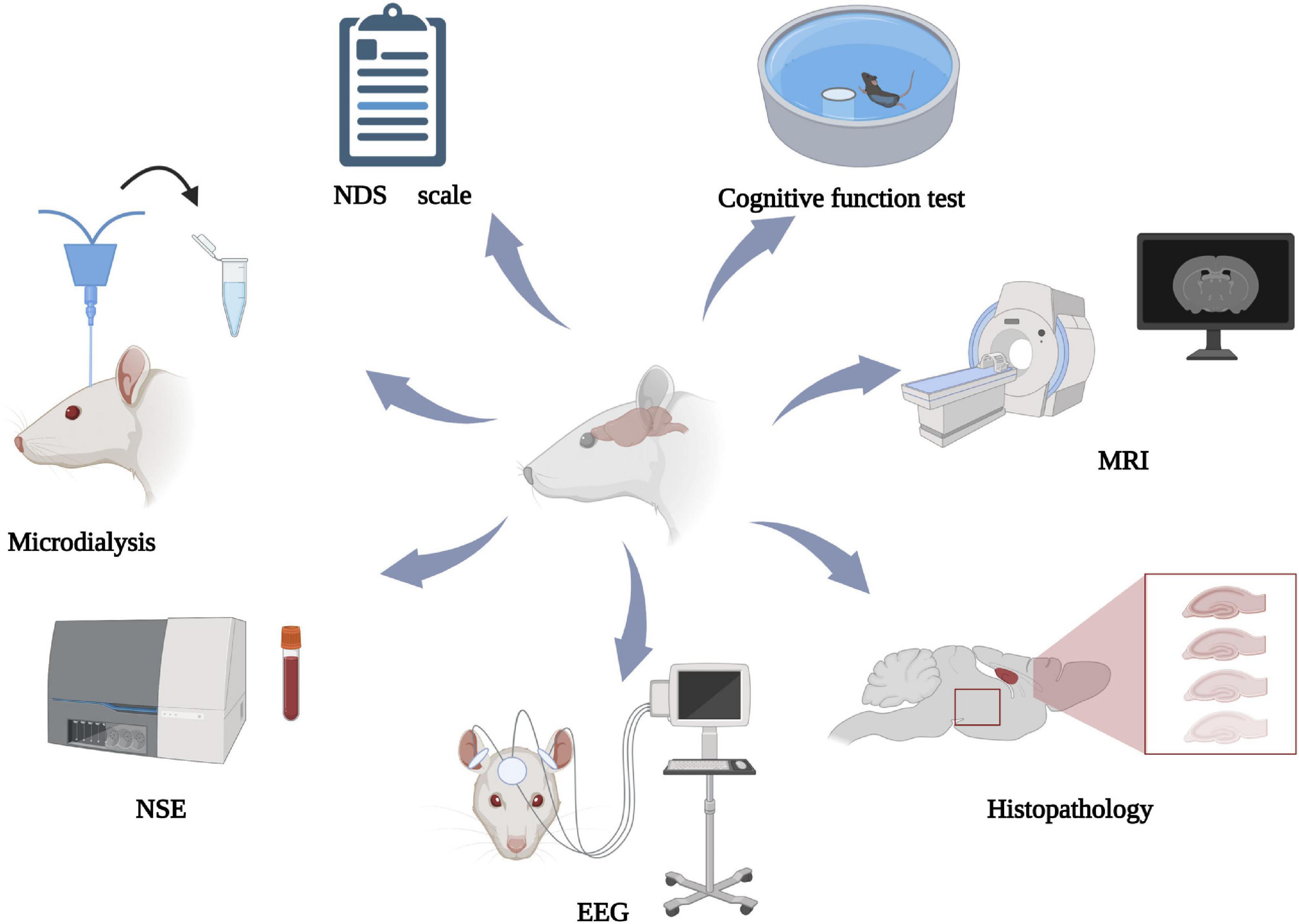
Asphyxiation Cardiac Arrest
Asphyxiation Cardiac Arrest - The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,.
Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies.
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies.
Frontiers Rat model of asphyxiainduced cardiac arrest and resuscitation
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or.
Frontiers Rat model of asphyxiainduced cardiac arrest and resuscitation
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Experimental animal models are valuable for.
Frontiers Rat model of asphyxiainduced cardiac arrest and resuscitation
Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this.
Synergistic Effects of Moderate Therapeutic Hypothermia and
Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,. Cardiac arrest as a result.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear. A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with.
Asphyxiaactivated corticocardiac signaling accelerates onset of
A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. Yet the pathophysiological mechanisms of this injury remain unclear. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with.
Cardiac Arrest Induced by Asphyxia Versus Ventricular Fibrillation
A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. Cardiac arrest as a result of asphyxia or. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard.
Yet The Pathophysiological Mechanisms Of This Injury Remain Unclear.
A complete airway obstruction results in pea and cardiac arrest within 8 minutes. Experimental animal models are valuable for exploring the etiologies. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiologic differences between dysrhythmic and asphyxial cardiac arrest in the. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic mechanisms,.