Brain Injury After Cardiac Arrest
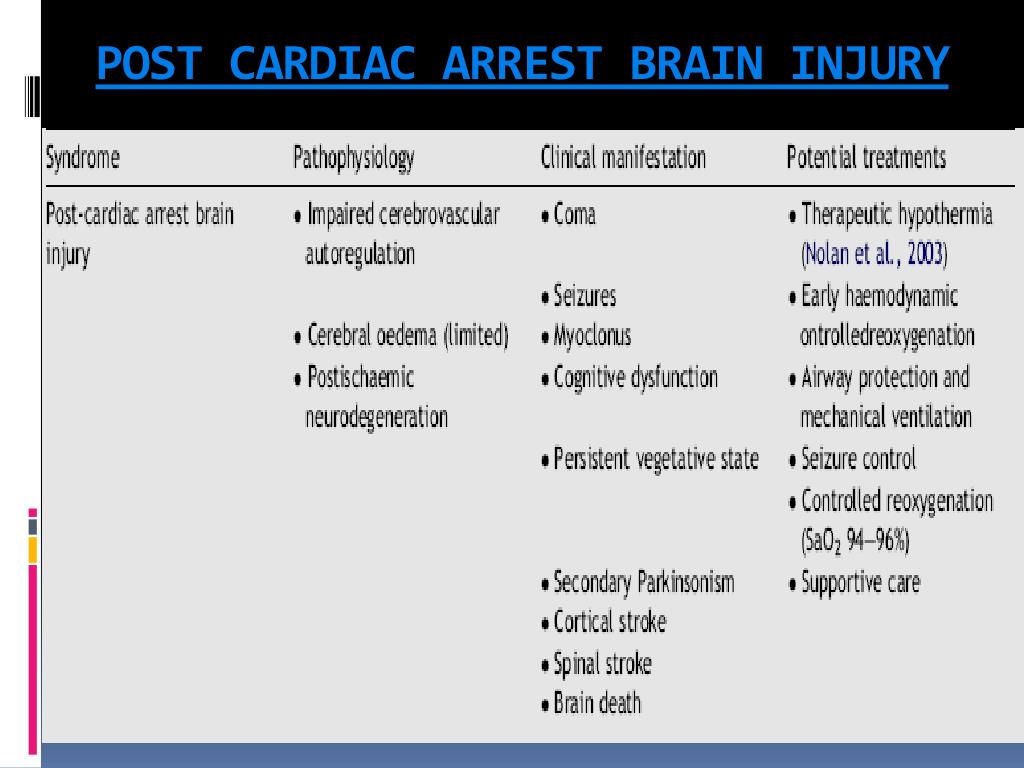
Brain Injury After Cardiac Arrest - In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and.
PPT Post cardiac arrest SYNDROME and post ROSC care PowerPoint
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. Most people who experience cardiac arrest.
PPT Post cardiac arrest SYNDROME and post ROSC care PowerPoint
In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In.
Frontiers Long Term Cognitive Function After Cardiac Arrest A Mini
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. In.
Understanding Brain Injury after Cardiac Arrest Sudden Cardiac Arrest UK
In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as.
Hirsch Brain Injury after Cardiac Arrest Management, Prognosis, and
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. In.
Neuroimaging of hypoxic ischemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Two
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma,.
During a cardiac arrest there are two stages of brain injury https
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. In.
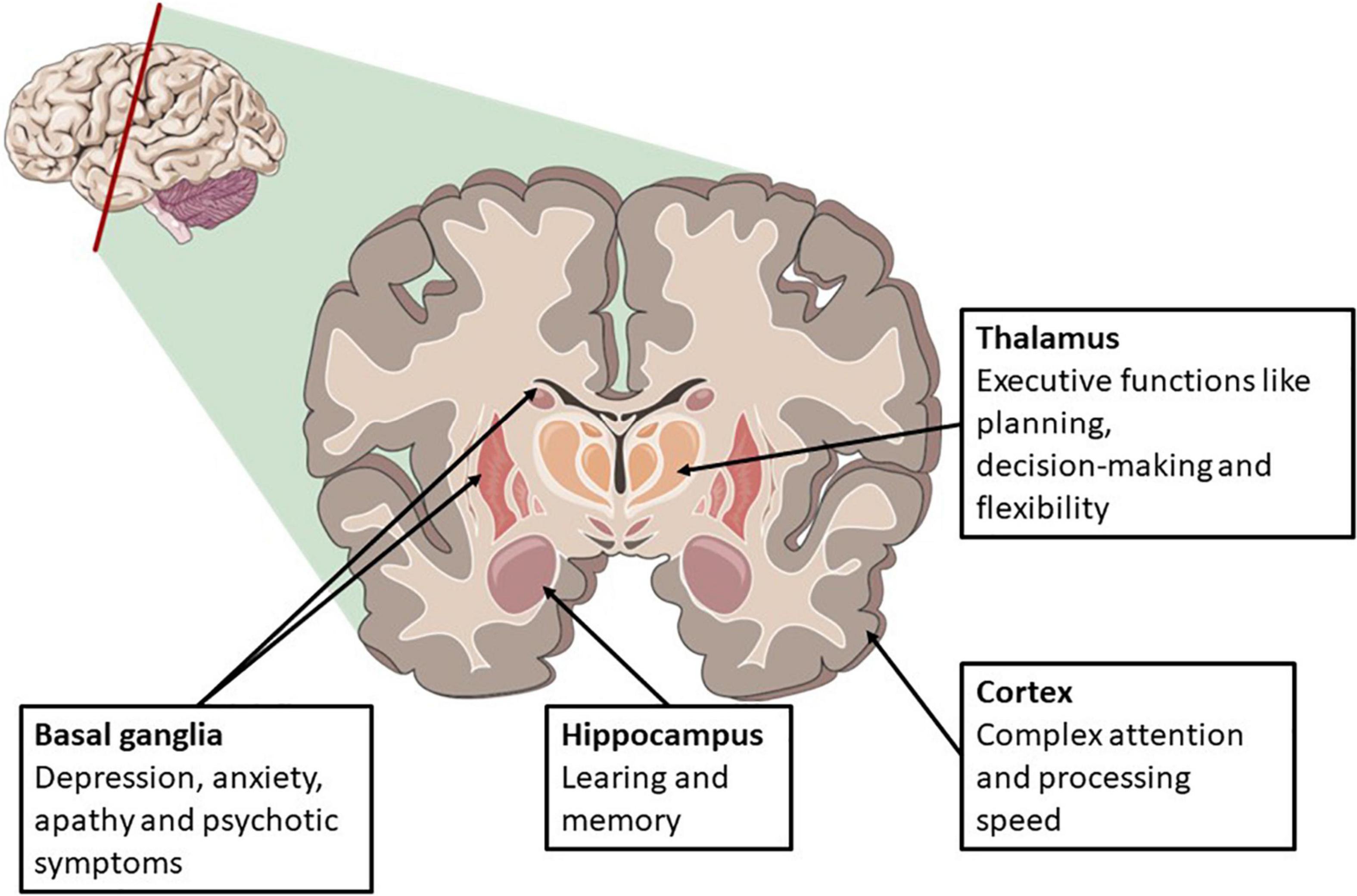
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means.
Effective Strategies To Minimise Brain Injury After Resuscitation Include Early Intervention With Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation And.
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, pcabi manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.