Cardiopulmonary Arrest In Infants
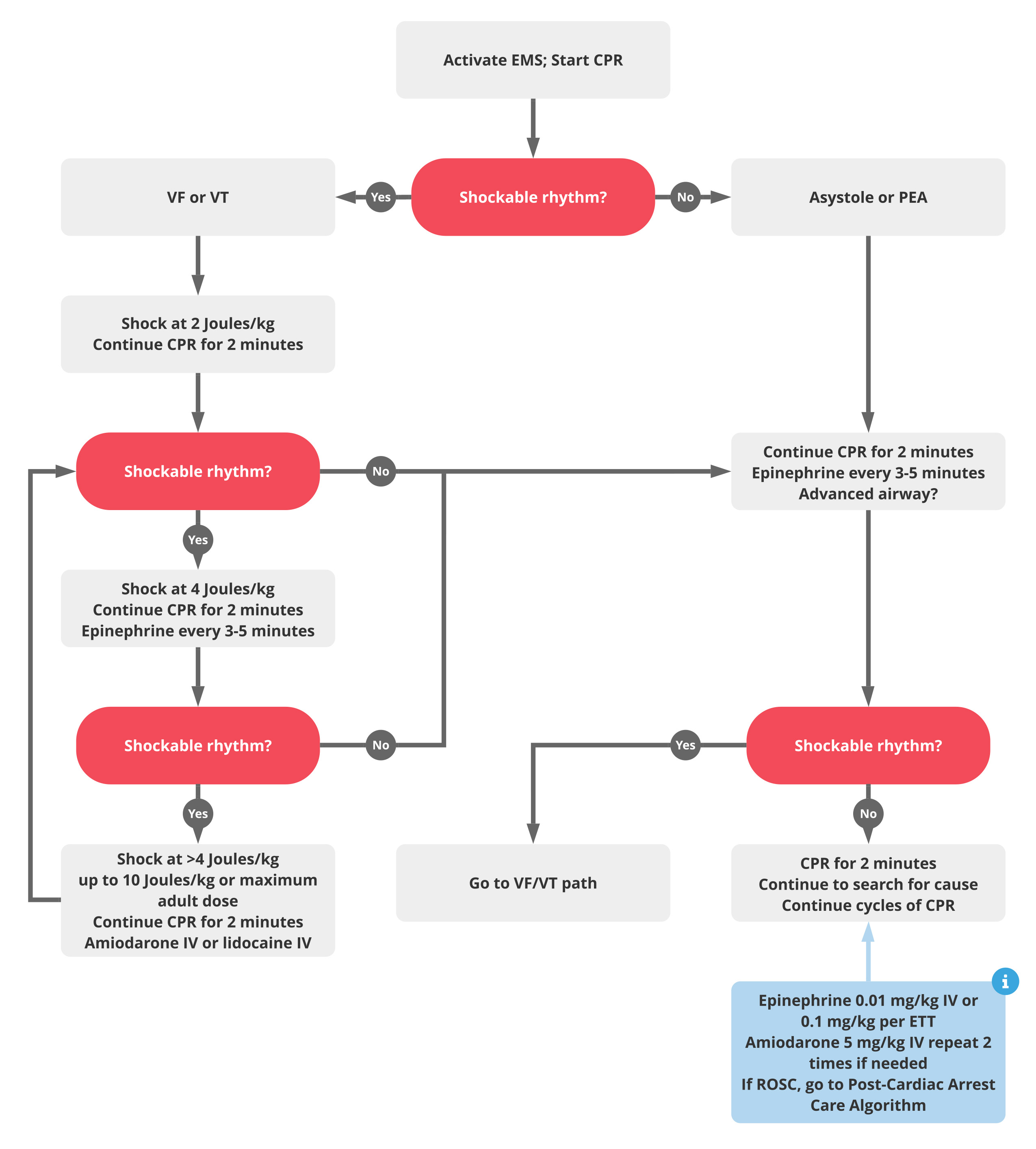
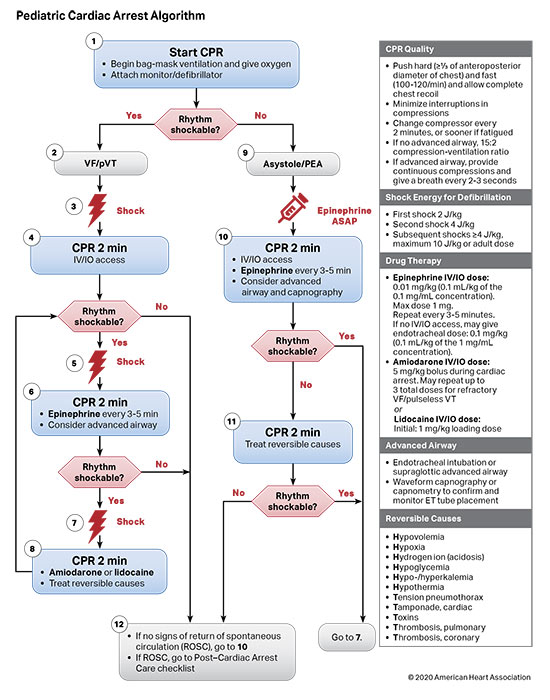
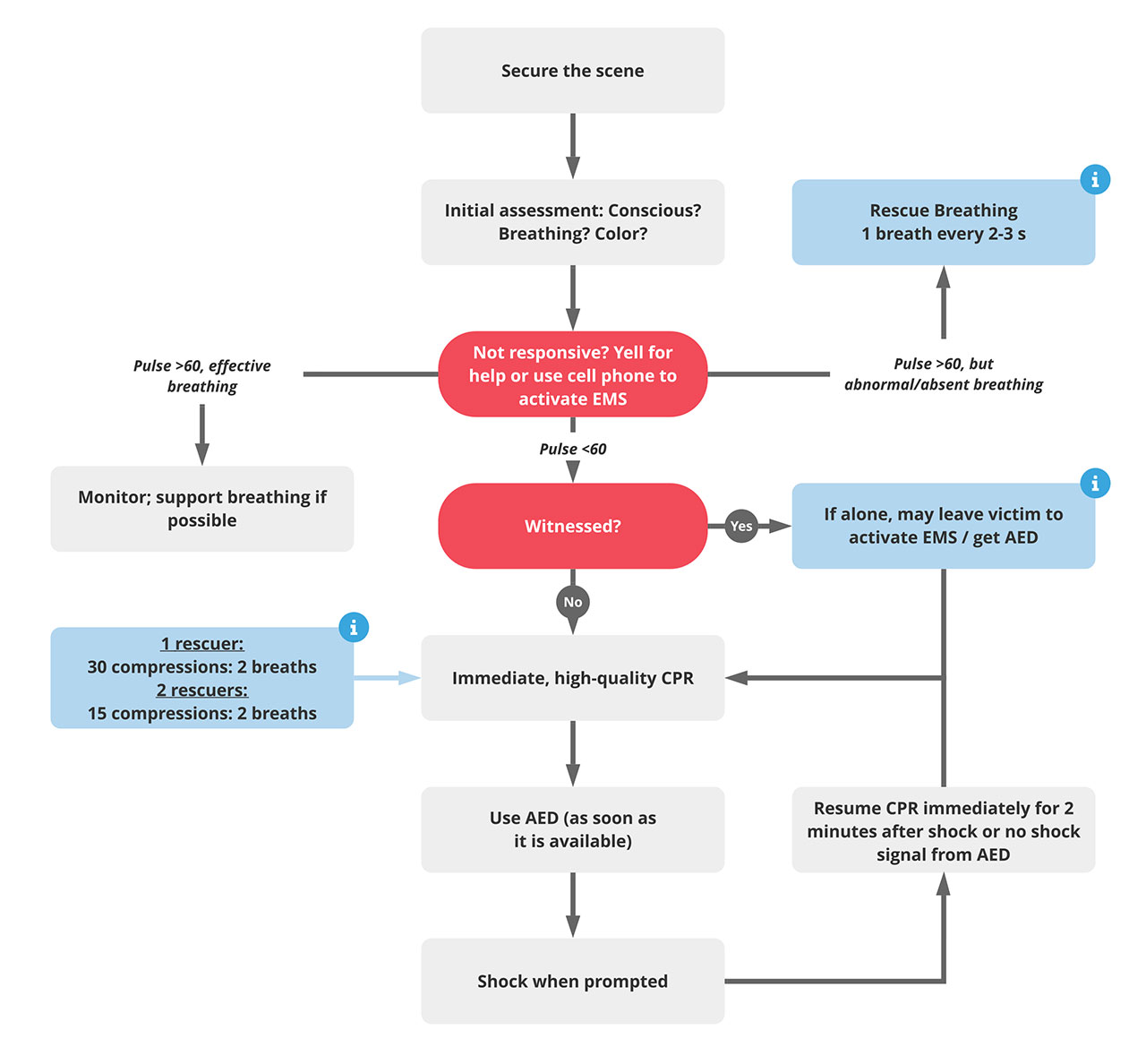
Cardiopulmonary Arrest In Infants - Learn the signs of cardiac arrest in infants and how to help with these steps from the red cross. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest.
Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Learn the signs of cardiac arrest in infants and how to help with these steps from the red cross. However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest.
In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Learn the signs of cardiac arrest in infants and how to help with these steps from the red cross.
Part 11 Pediatric Basic Life Support and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70%.
Part 13 Pediatric Basic Life Support Circulation
However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in.
Sudden cardiac arrest in children Warning signs and symptoms
However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Unlike in.
Pediatric PostCardiac Arrest Care A Scientific Statement From the
Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. However, in.
PALS Certification Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Learn the signs of cardiac arrest in infants and how to help.
Part 4 Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support American Heart
In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Learn the signs of cardiac arrest in infants and how to help.
New rules on saving kids stricken with cardiac arrest
Learn the signs of cardiac arrest in infants and how to help with these steps from the red cross. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with.
Infant BLS Algorithm Training and Guidelines
Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70%.
Part 11 Pediatric Basic Life Support and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. However, in older children, trauma and.
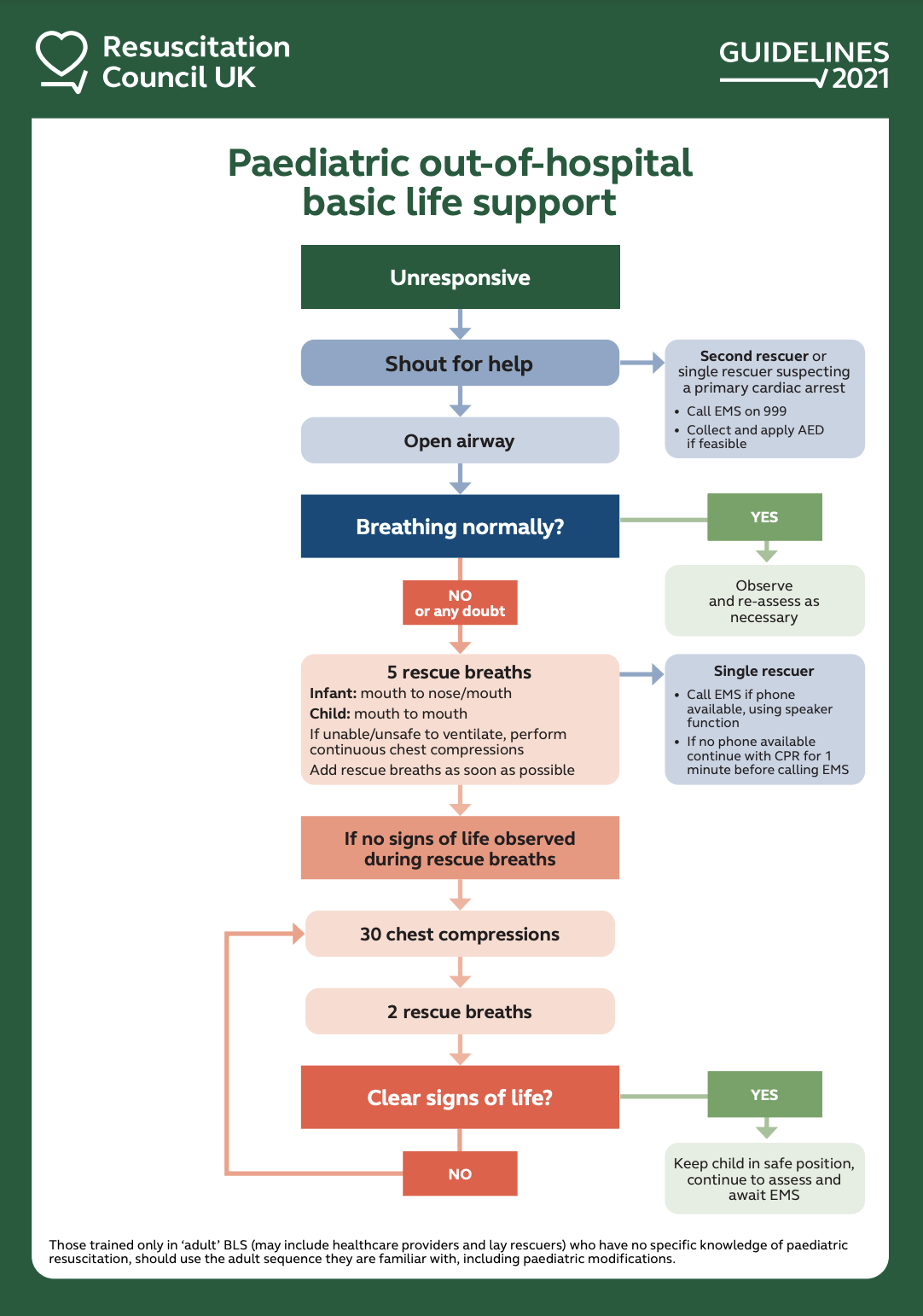
Paediatric basic life support Guidelines Resuscitation Council UK
In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. Unlike in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in rare in children and less likely to be a primary cardiac event. However, in older children, trauma and respiratory failure. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in.
Unlike In Adults, Cardiopulmonary Arrest In Rare In Children And Less Likely To Be A Primary Cardiac Event.
Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. In infants, sudden infant death syndrome (sids) is a leading cause of cardiac arrest. Be prepared and sign up for a first aid course. Learn the signs of cardiac arrest in infants and how to help with these steps from the red cross.