Does Cardiac Arrest Cause Brain Damage
Does Cardiac Arrest Cause Brain Damage - Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
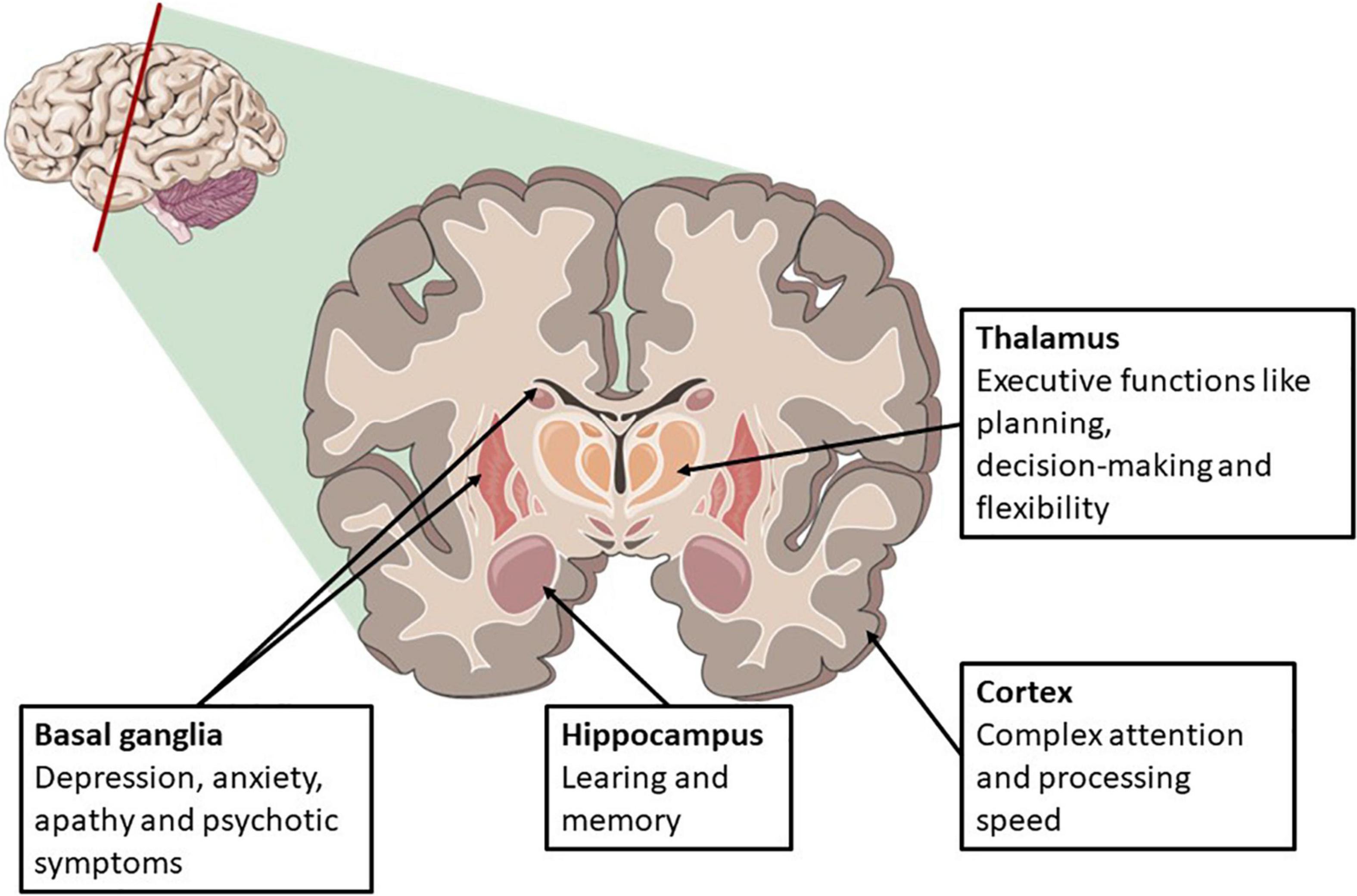
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality.
Frontiers Long Term Cognitive Function After Cardiac Arrest A Mini
Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Out‐of‐Hospital
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and.
The Lancet on Twitter "Brain injury after cardiac arrest remains a
Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest The Lancet
Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality.
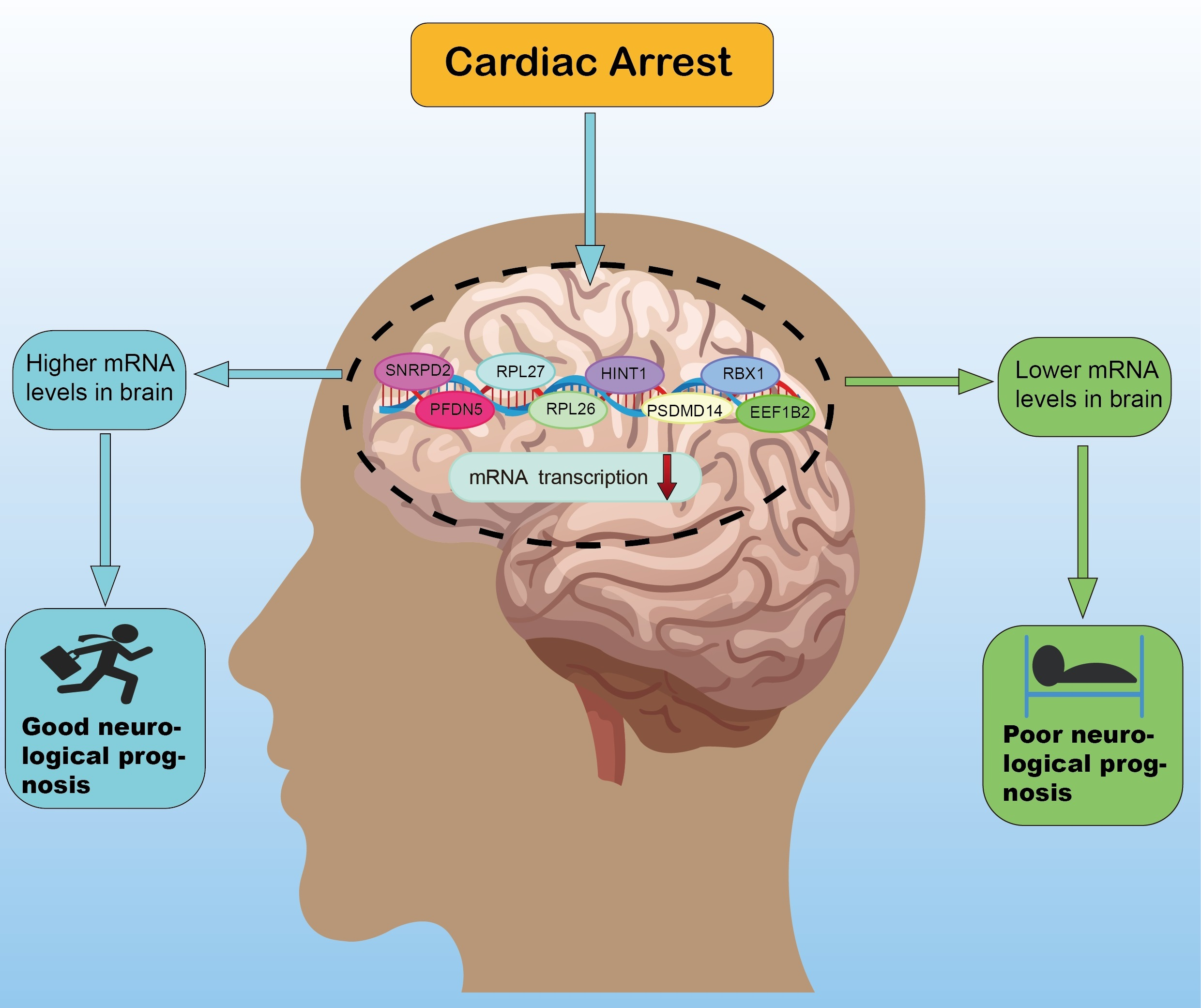
Identification and Validation of Novel Potential Pathogenesis and
Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
Brain Hypoxia Is Associated With Neuroglial Injury in Humans Post
Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
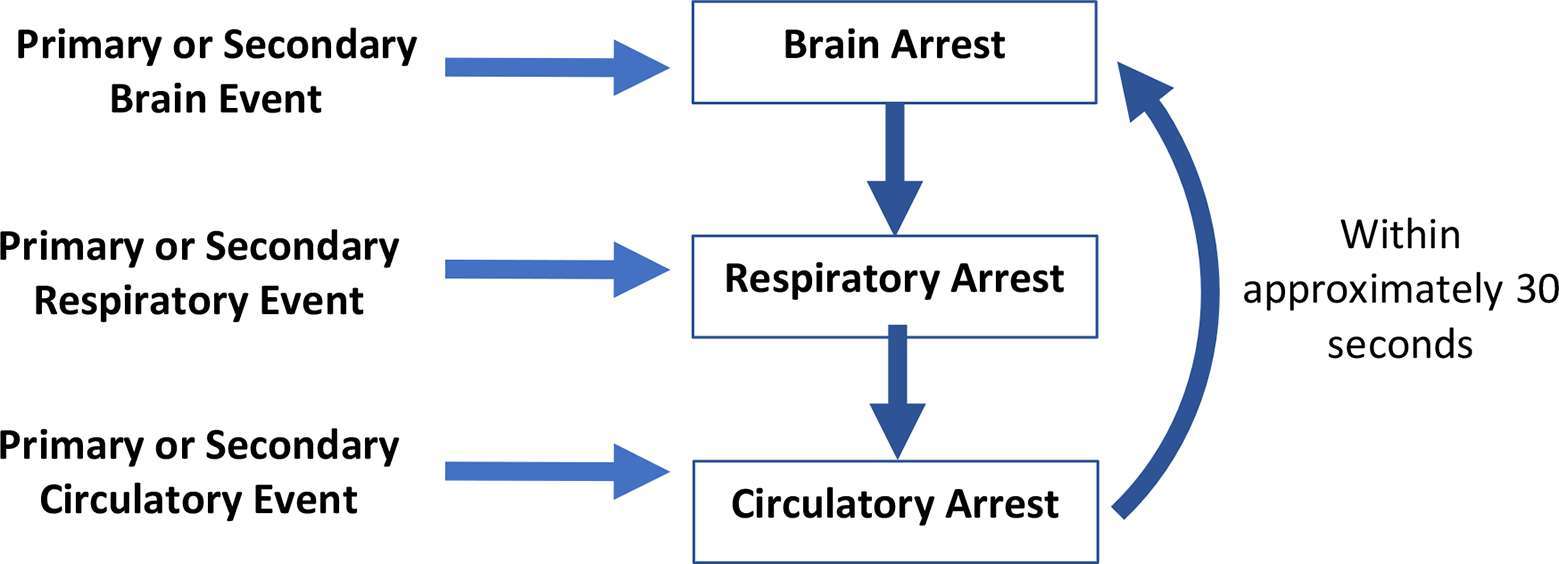
Frontiers Circulatory Arrest, Brain Arrest and Death Determination
Despite advances over time in cardiac arrest management and. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
Despite Advances Over Time In Cardiac Arrest Management And.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is a catastrophic event with high morbidity and mortality.