Energy Availability Formula
Energy Availability Formula - Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. For example, an energy availability of 45. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. Specifically, ea is given by the formula:
Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. For example, an energy availability of 45. For example, let's consider a 10%. Specifically, ea is given by the formula: Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed.
Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. For example, let's consider a 10%. For example, an energy availability of 45. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. Specifically, ea is given by the formula:
Energy Balance Equation And Heat Transfer Process
For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. Specifically, ea is given by the formula: Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per.
Assessing Energy Requirements, Energy Balance and Energy Availability
Specifically, ea is given by the formula: Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. For example, an energy availability of 45. For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed.
Theory of Wave Energy & Availability
Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. For example,.
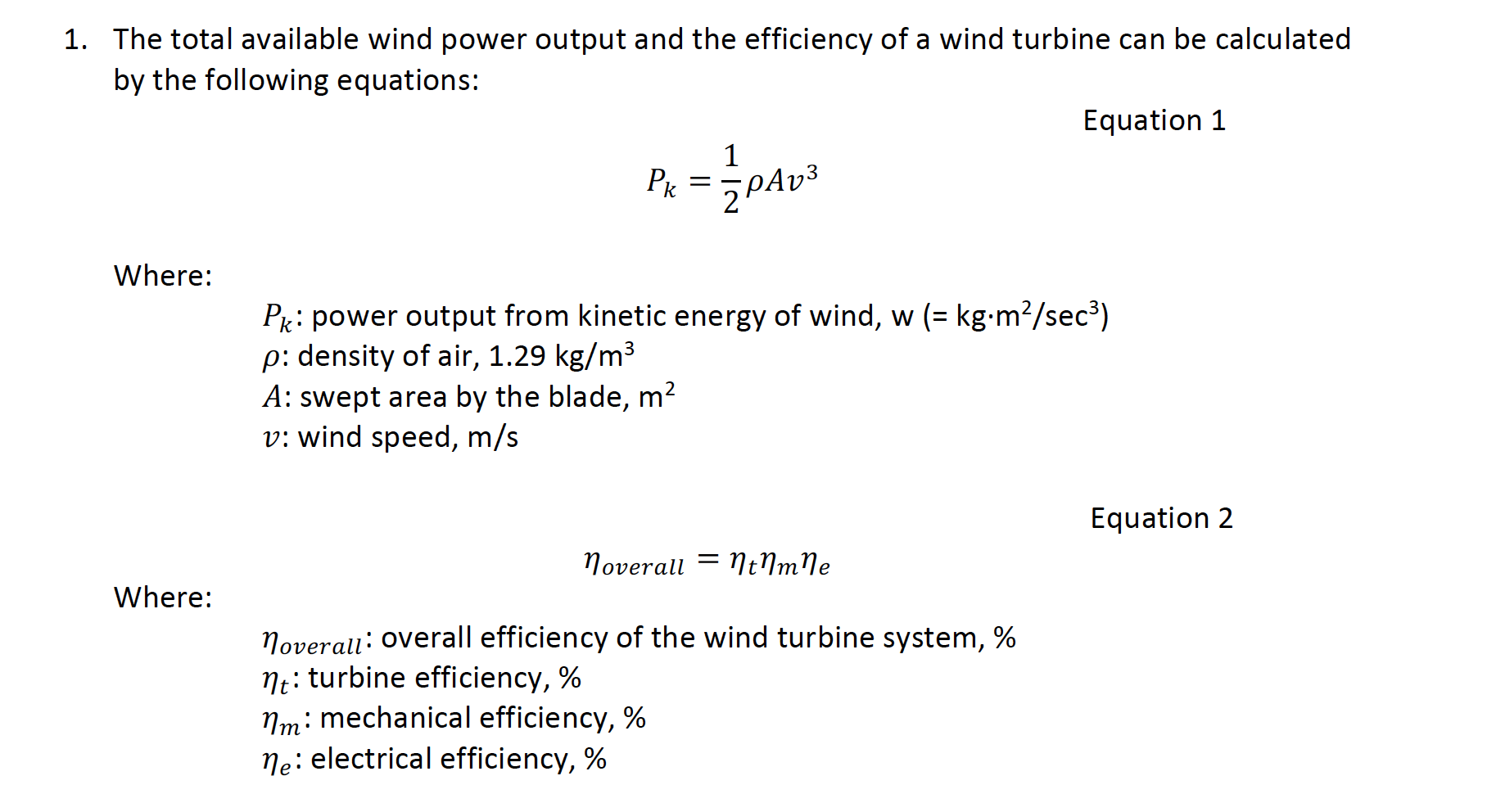
1. The total available wind power output and the
For example, an energy availability of 45. For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. Specifically, ea is given by the formula:
PPT Particle Accelerators PowerPoint Presentation ID1891615
For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. Specifically, ea is given by the formula: Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure.
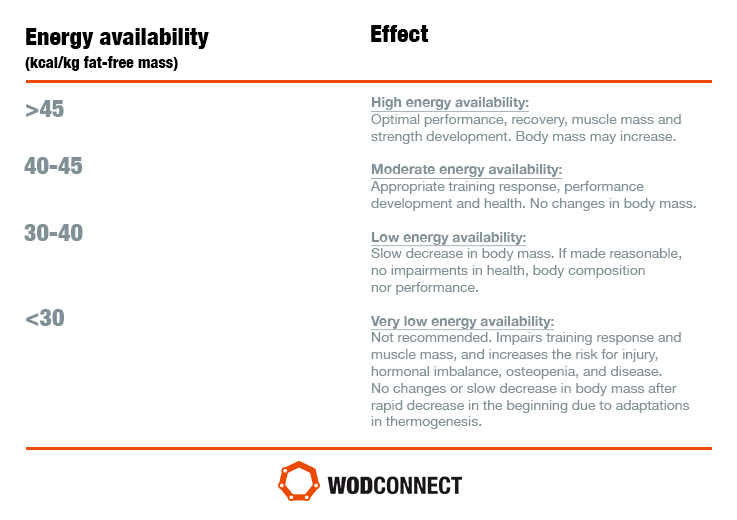
Boosting performance with appropriate energy availability WODconnect
For example, an energy availability of 45. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from.
Boosting performance with appropriate energy availability WODconnect
Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. Specifically, ea is given by the formula: Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. For.
Theory of Wave Energy & Availability
Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. For example, an energy availability of 45. For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. Specifically, ea is given by the formula:
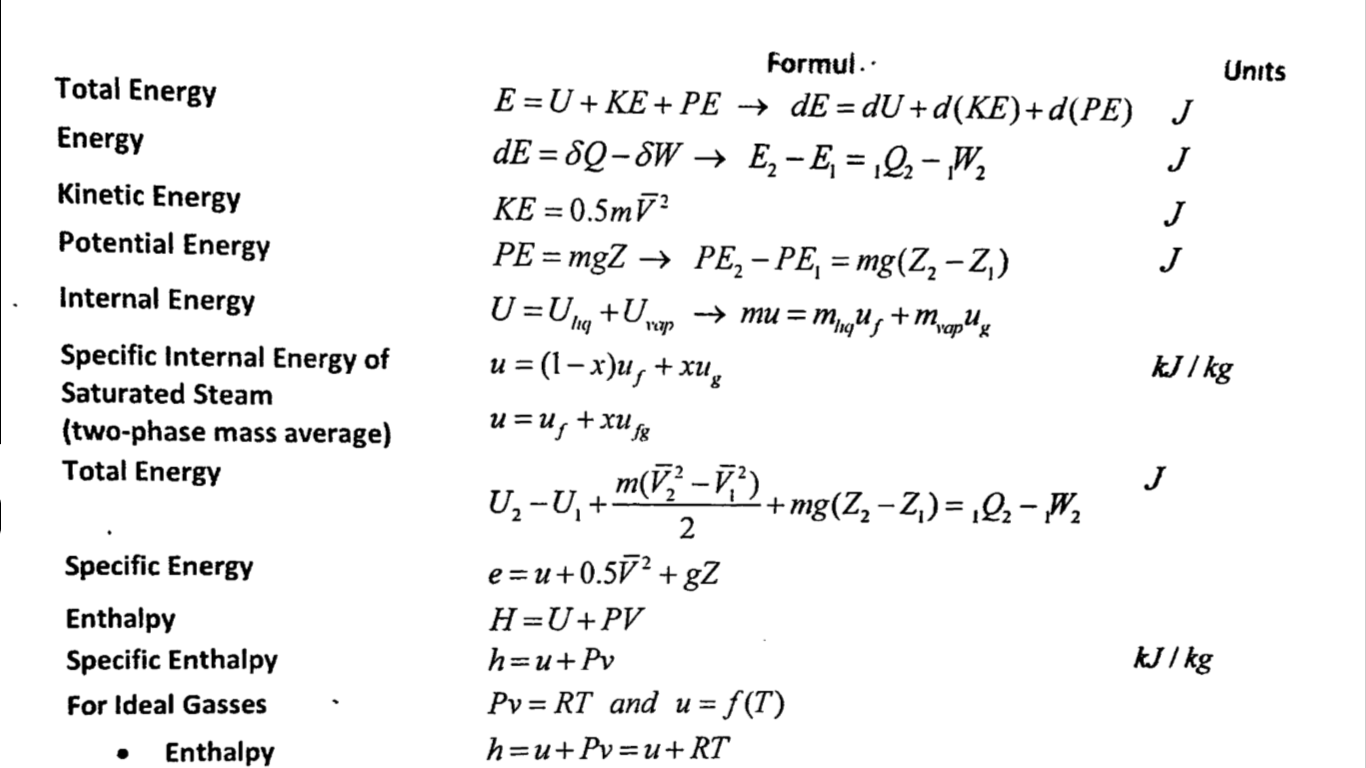
Thermodynamics 2 Equation Sheet
Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. Specifically, ea is given by the formula: Energy availability is calculated by dividing the amount of calories left over from training by lean body mass. For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure.
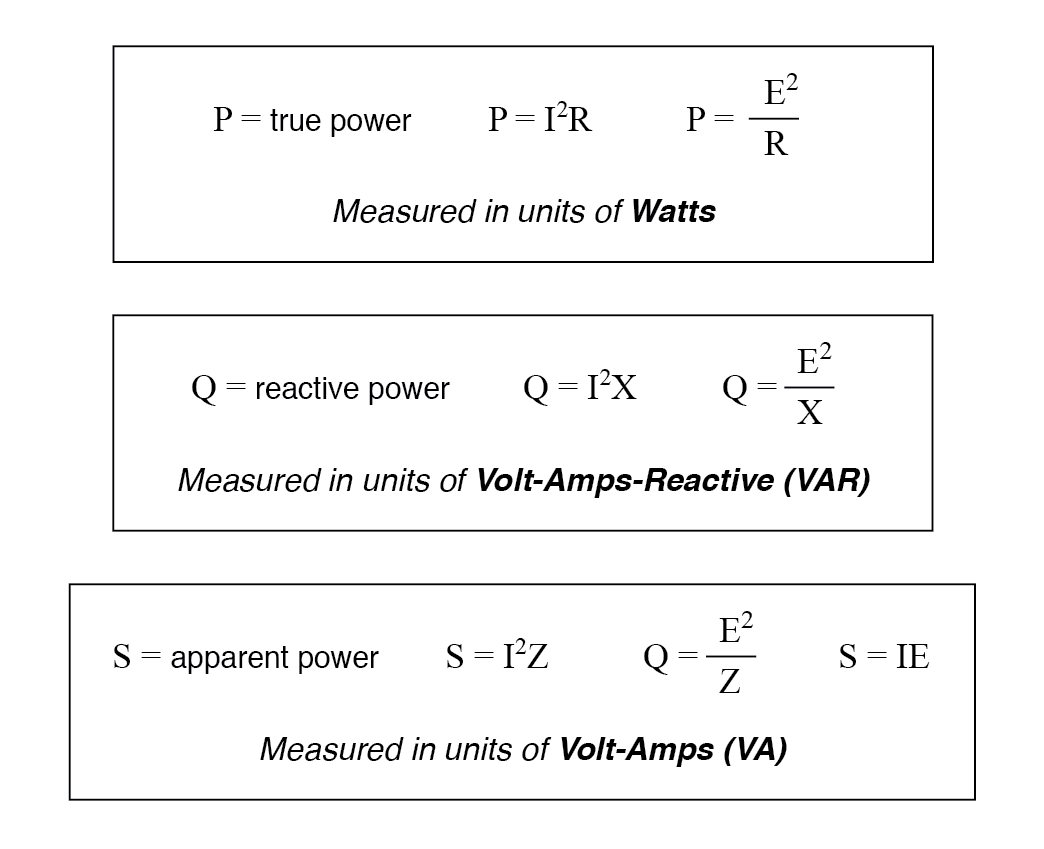
True, Reactive, and Apparent Power Power Factor Electronics Textbook
For example, let's consider a 10%. Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. Energy availability (ea) is thus calculated as energy intake (ei) minus exercise energy expenditure (eee) and is commonly expressed. Specifically, ea is given by the formula: For example, an energy availability of 45.
Energy Availability (Ea) Is Thus Calculated As Energy Intake (Ei) Minus Exercise Energy Expenditure (Eee) And Is Commonly Expressed.
For example, an energy availability of 45. Specifically, ea is given by the formula: Energy availability is expressed in a calculation as calories per kilogram of fat free mass. For example, let's consider a 10%.