Post Cardiac Arrest Brain Injury
Post Cardiac Arrest Brain Injury - Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. It is most likely that ongoing advances in.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
Brain Hypoxia Is Associated With Neuroglial Injury in Humans Post
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. It is most likely that ongoing advances in.
Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Out‐of‐Hospital
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.
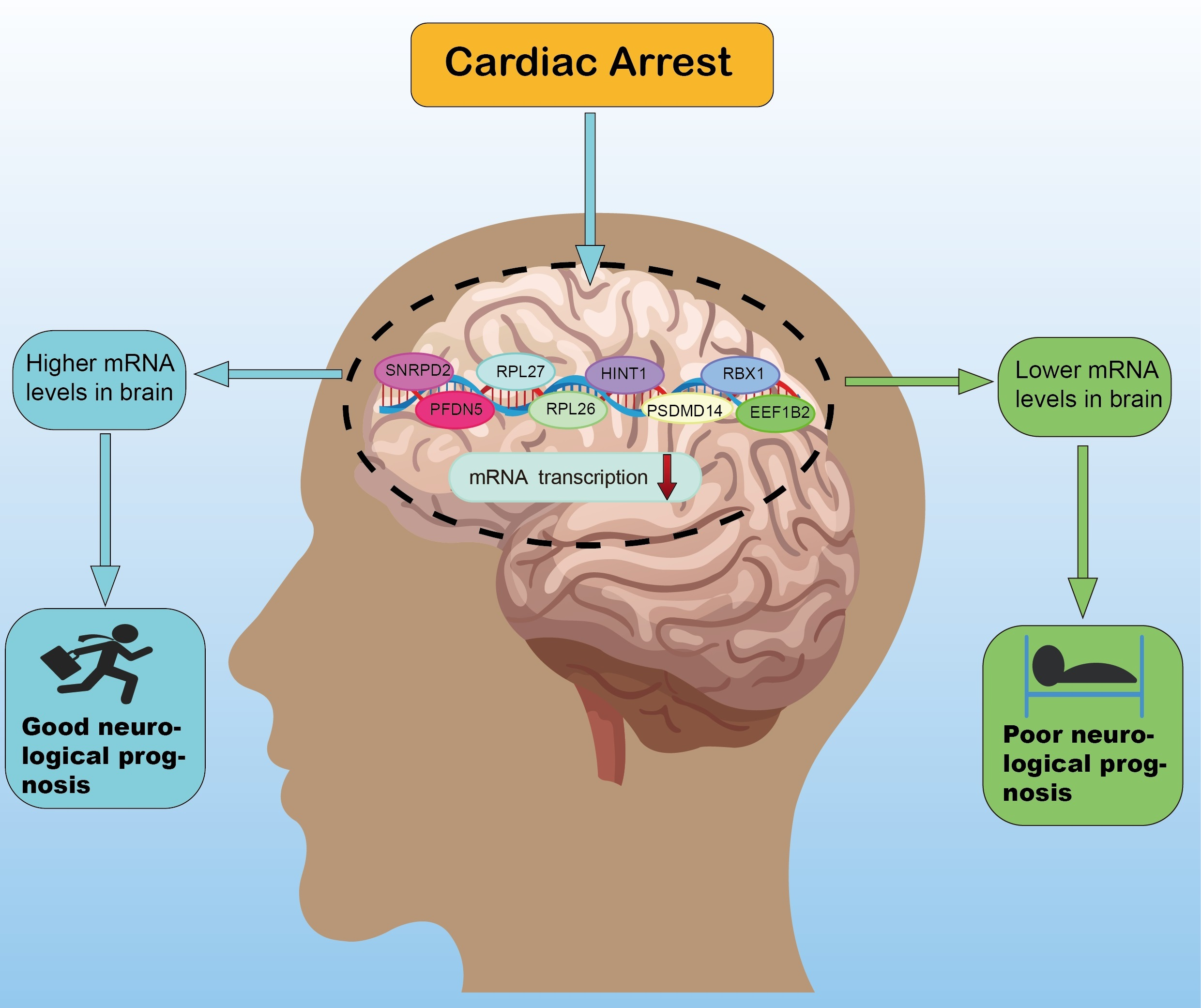
Identification and Validation of Novel Potential Pathogenesis and
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field.
Frontiers Long Term Cognitive Function After Cardiac Arrest A Mini
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. It is most likely that ongoing advances in.
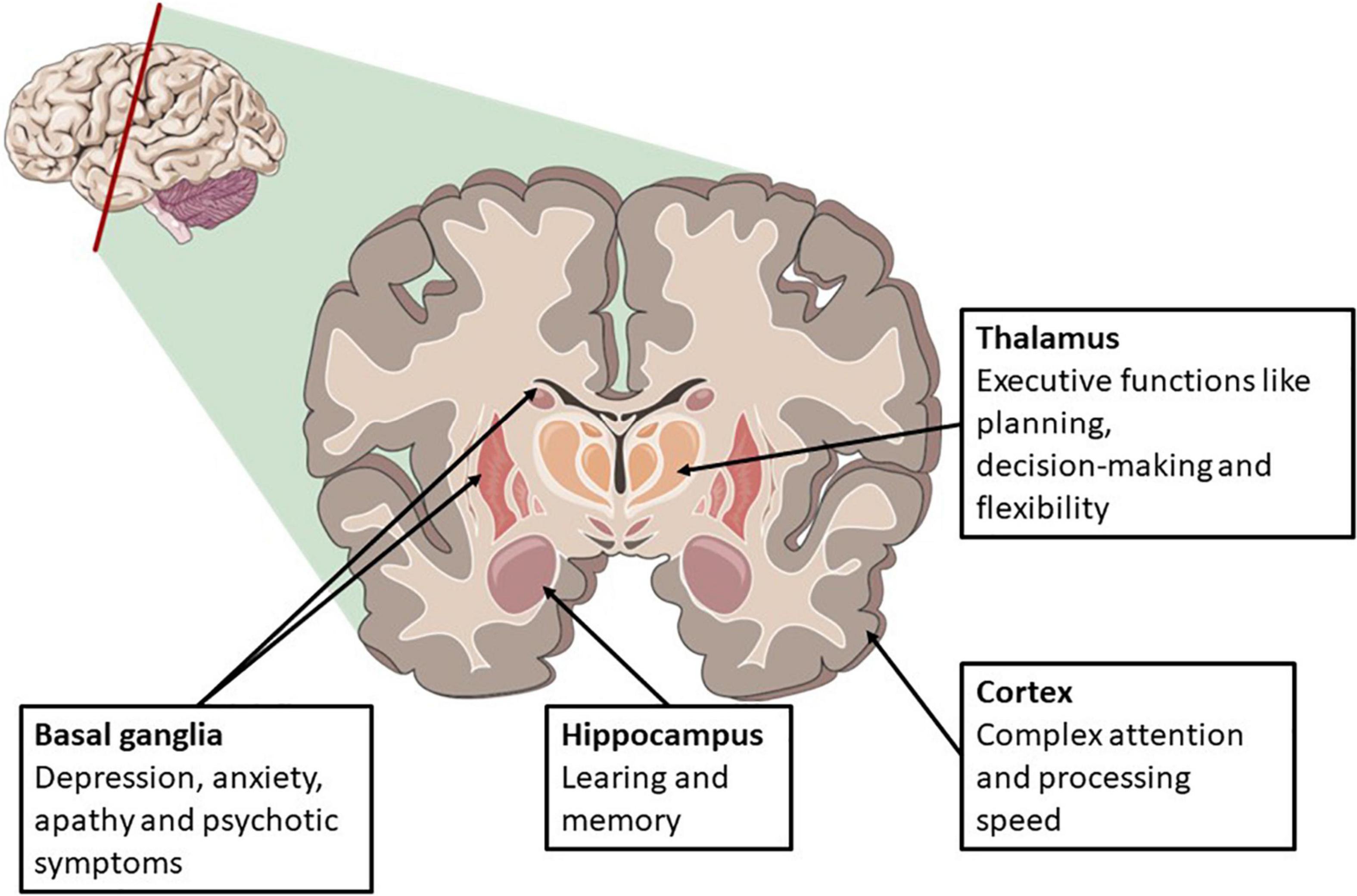
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
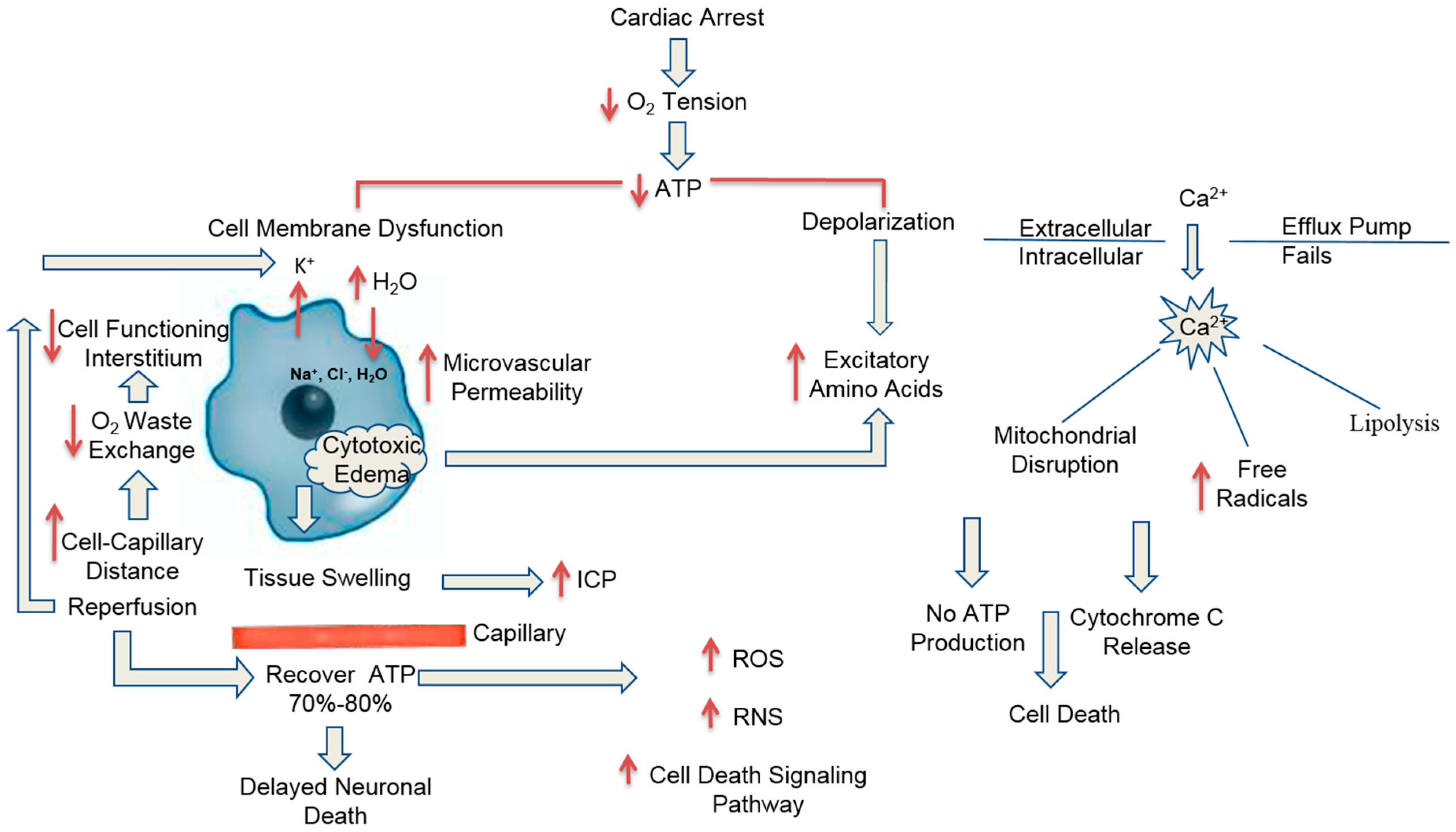
Pathophysiology and the Monitoring Methods for Cardiac Arrest
It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Effective strategies to minimise brain injury after resuscitation include early intervention with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and.
Effective Strategies To Minimise Brain Injury After Resuscitation Include Early Intervention With Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation And.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. It is most likely that ongoing advances in.