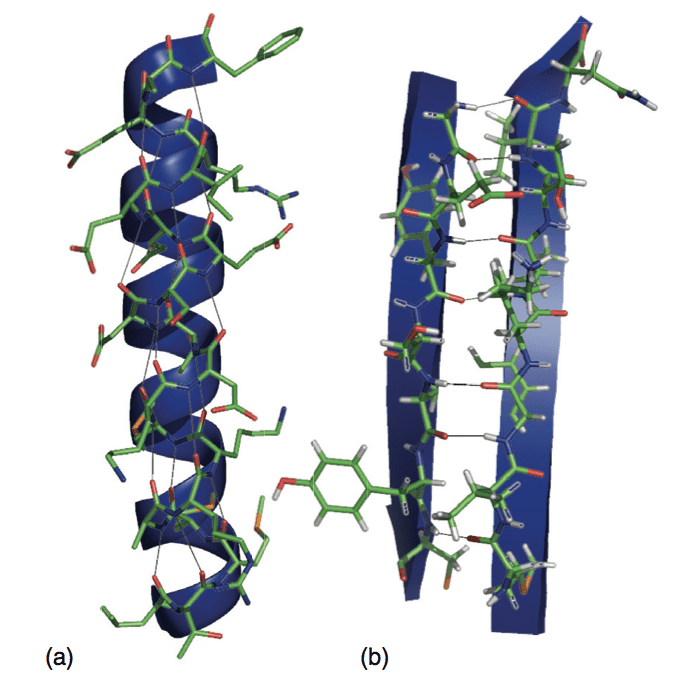Secondary Structure Of Protein Beta Sheet
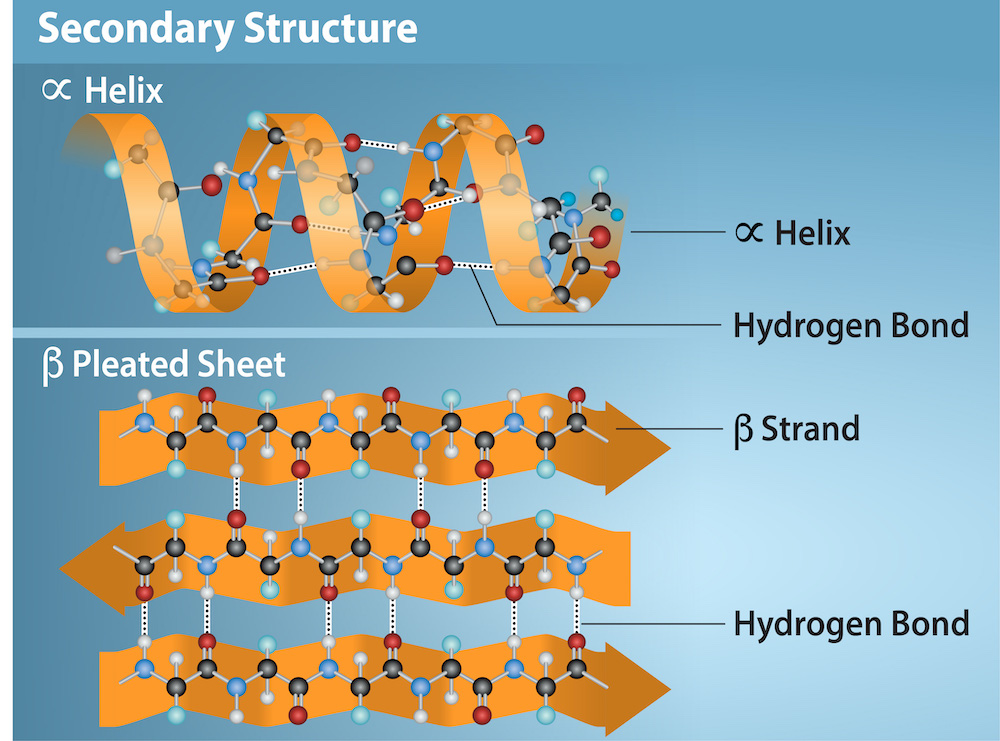
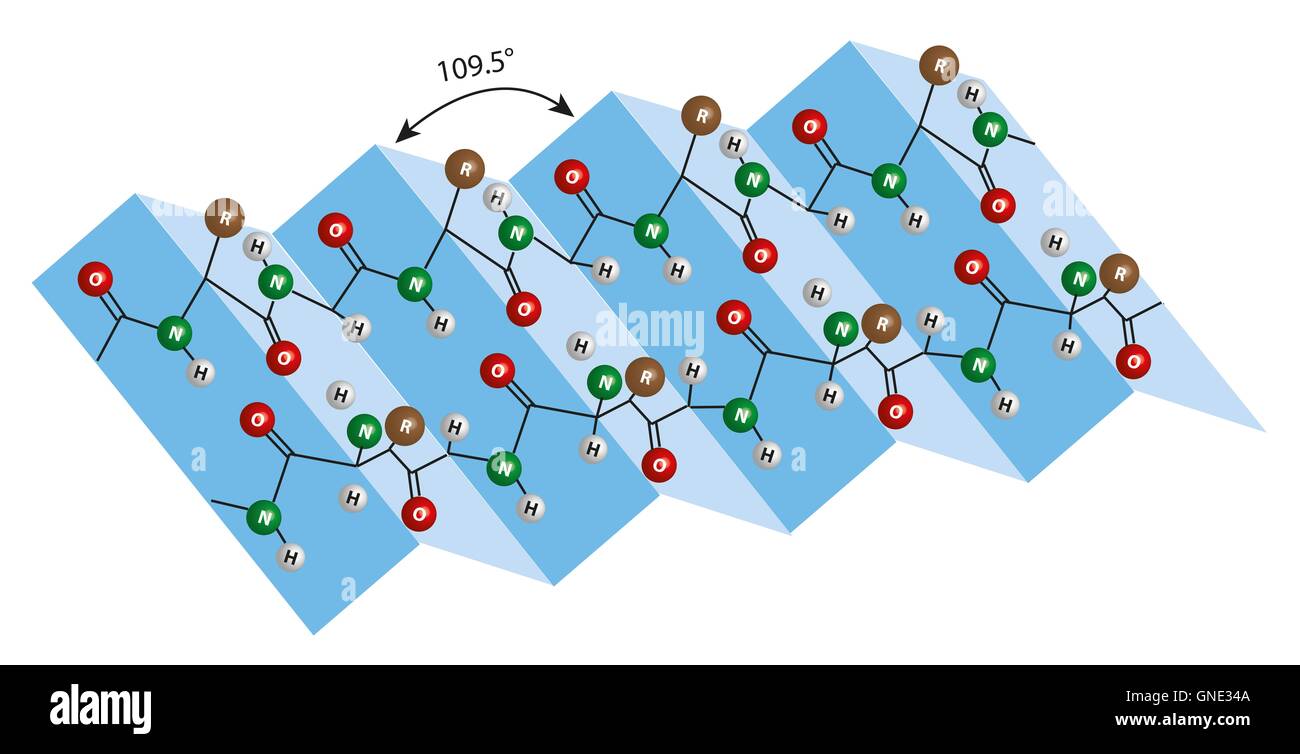
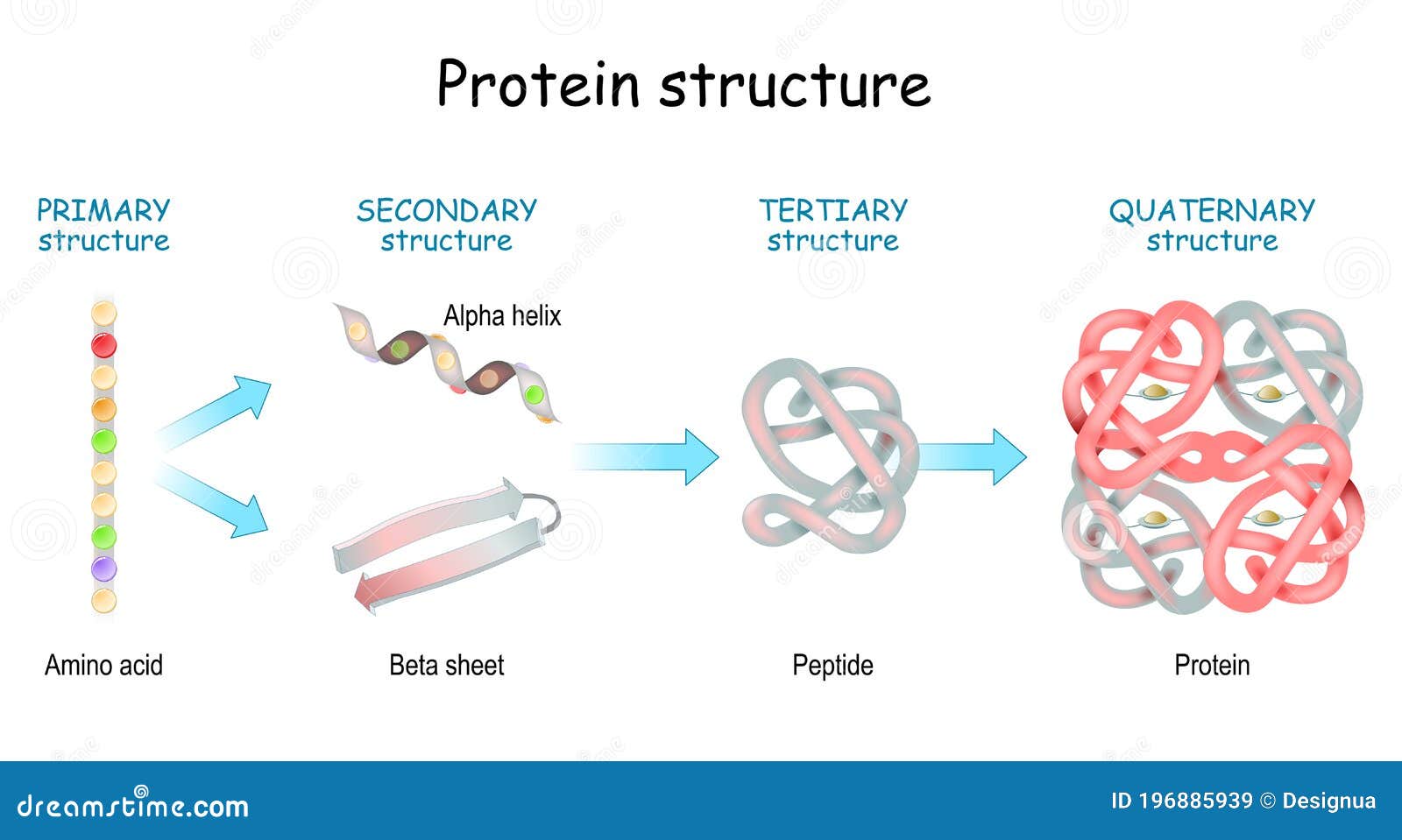
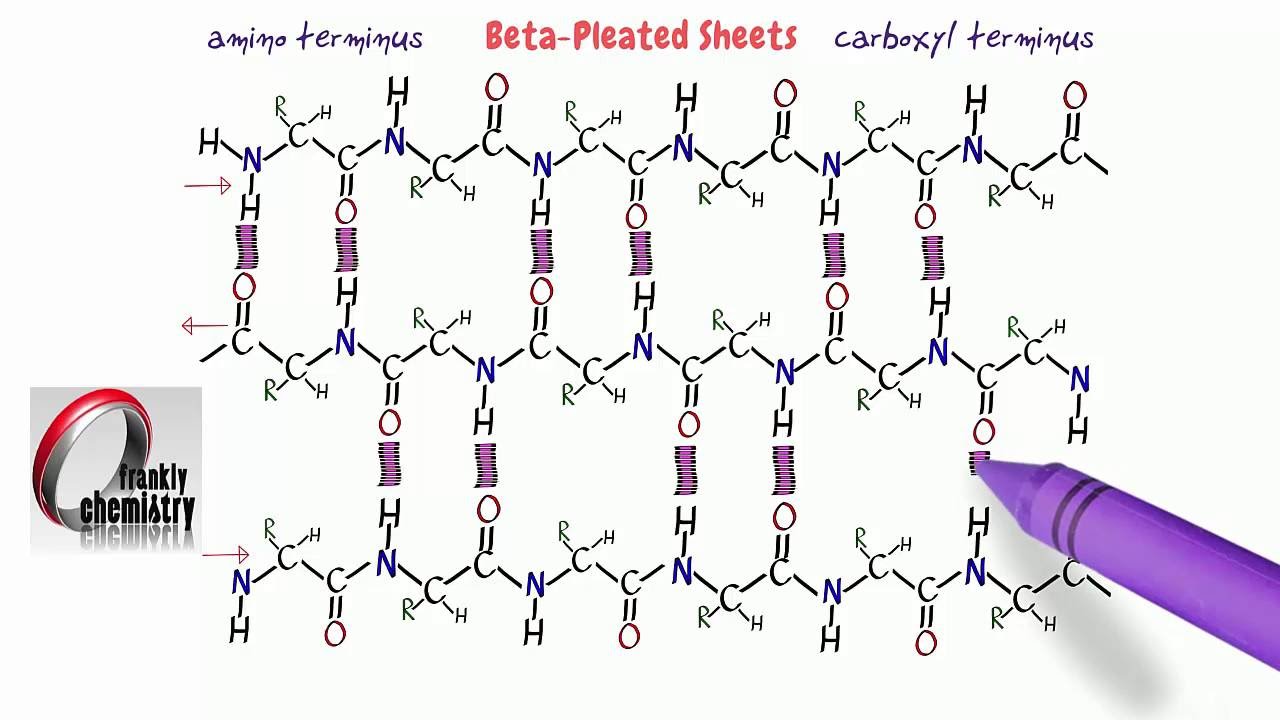
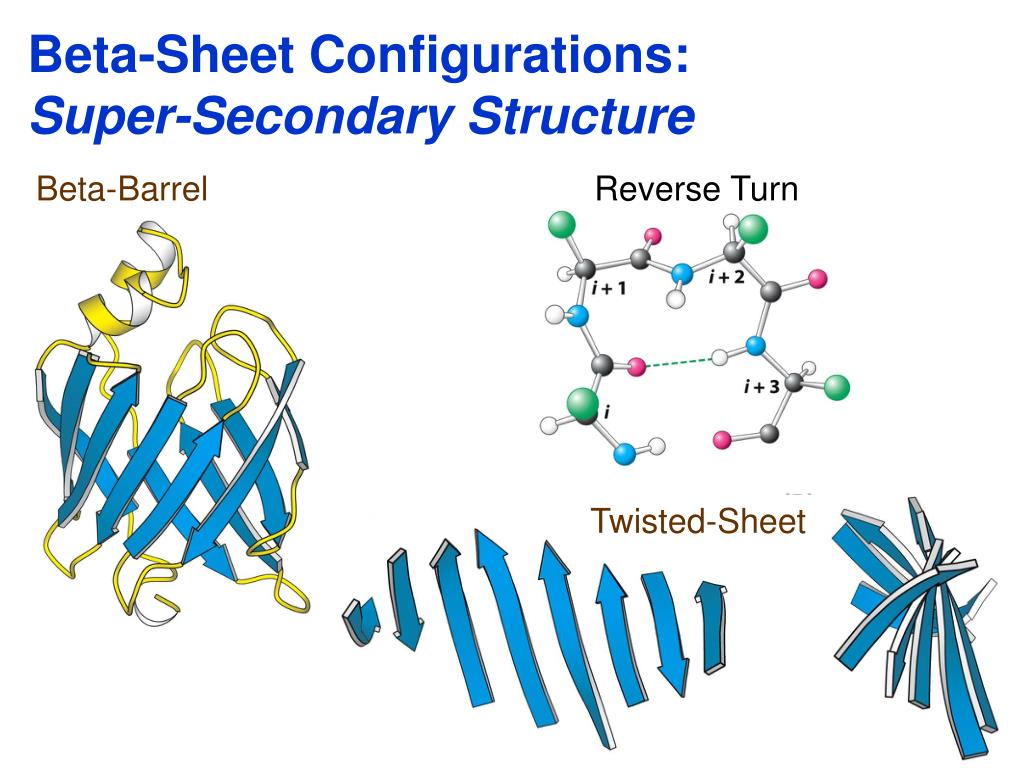
Secondary Structure Of Protein Beta Sheet - Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and.
Biochemistry Secondary Structure 2 The Beta Sheet ditki medical
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and.
1. Secondary structure of protein, αhelix and βpleated sheet [118
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and.
Secondary Protein Structure Beta Pleated Sheet
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains.
What Is A Beta Sheet
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains.
Protein Secondary Structure Alpha Helix And Beta Sheet
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).
α helix & β sheet Protein secondary structure
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).
What Are Beta Sheets Used For at Clifford Pannell blog
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains.
Amino Acids 8. The betapleated sheets secondary structure of Proteins
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).
PPT Proteins Amino Acid Chains PowerPoint Presentation, free
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains.
Protein Secondary Structure Is The Local Spatial Conformation Of The Polypeptide Backbone Excluding The Side Chains.
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).