Sinus Arrest Ecg
Sinus Arrest Ecg - Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. See a sample ekg rhythm. Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2.
Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. See a sample ekg rhythm. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg.
Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. See a sample ekg rhythm.
Sinus Arrest Sinus Pause Ecg Paper 12 Lead Stock Illustration
Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause.
Basic Ekg Reviewr2
See a sample ekg rhythm. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg,.
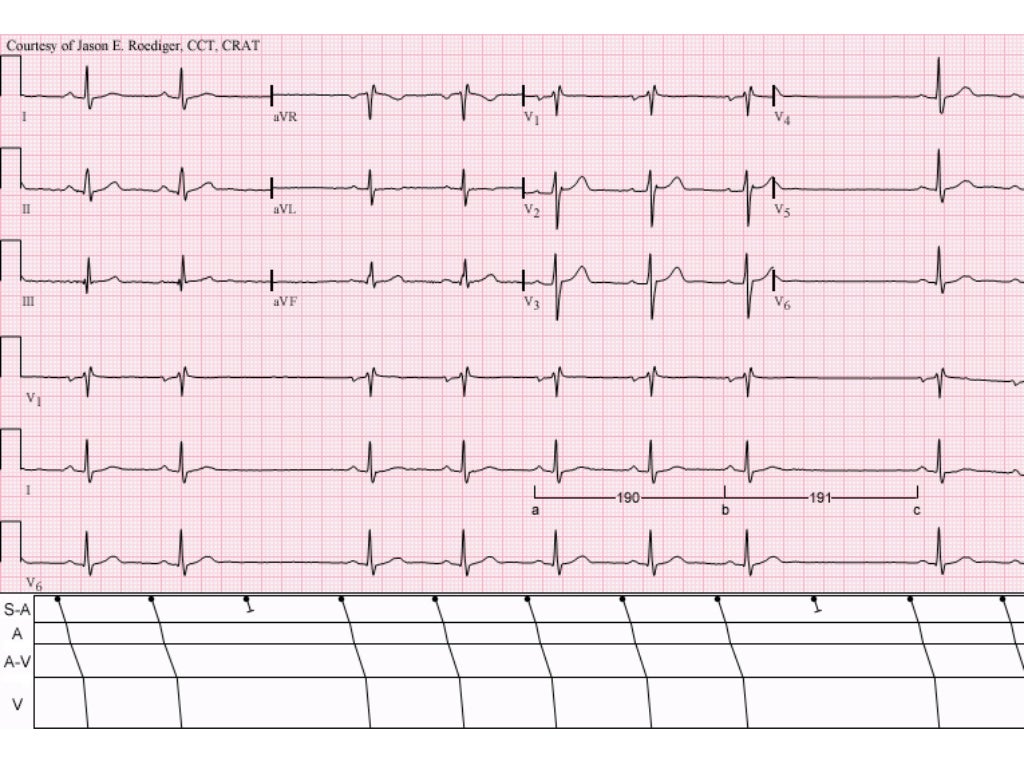
ECG Lecture Sinus arrest, sinoatrial exit block, AV block and escape…
Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. See a sample ekg rhythm. Learn how to identify sinus arrest,.
ECG Educator Blog Sinus Arrest
Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type.
Electrocardiogram Show Sinus Arrest Pattern. Stock Vector
See a sample ekg rhythm. Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type.
ECG Lecture Sinus arrest, sinoatrial exit block, AV block and escape…
Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. See a sample ekg rhythm. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may.
ECG Educator Blog Sinus Arrest
Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge.
ECG Lecture Sinus arrest, sinoatrial exit block, AV block and escape…
See a sample ekg rhythm. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the.
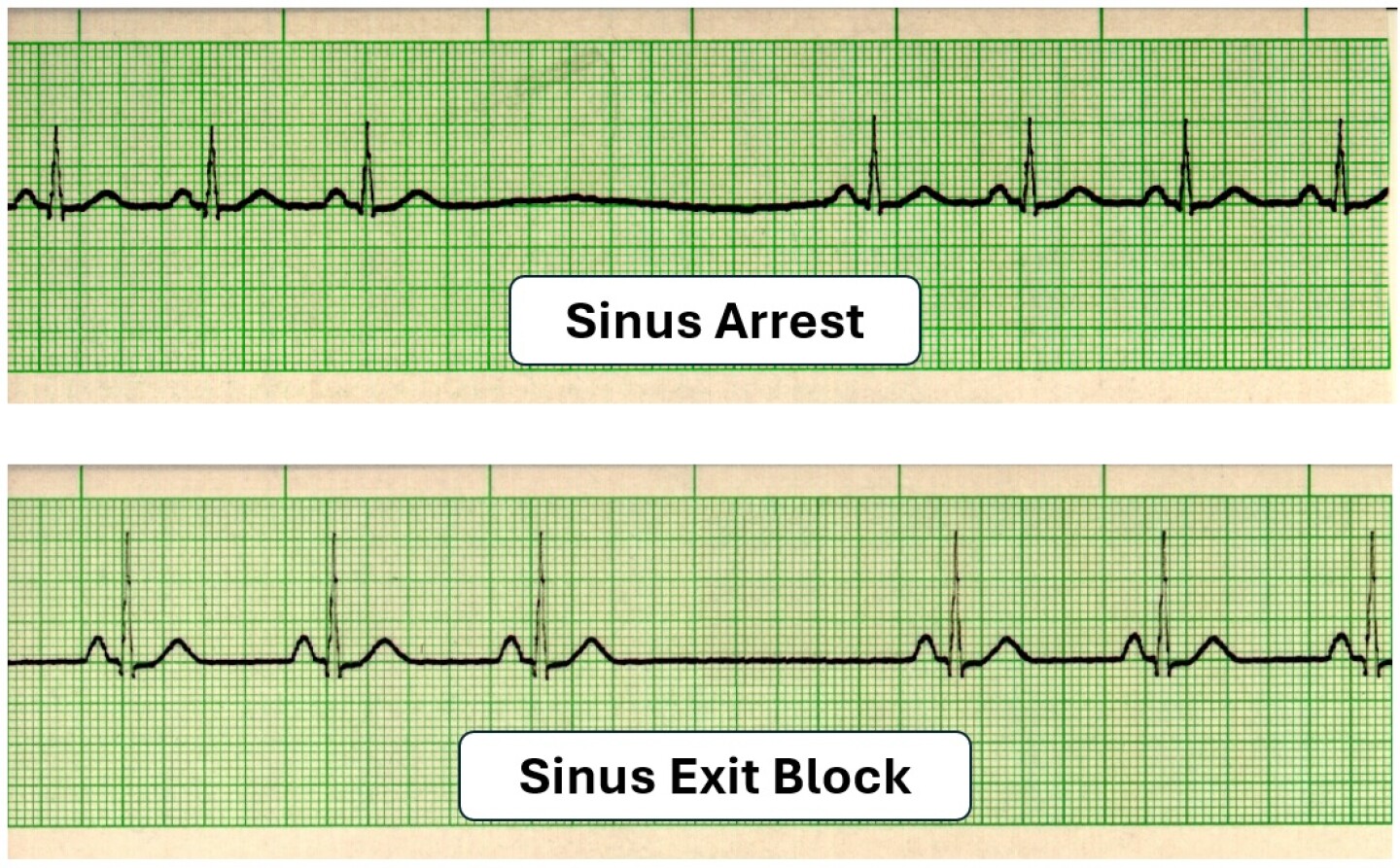
EKG Detective Sinus arrest vs. sinus exit block
Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of.
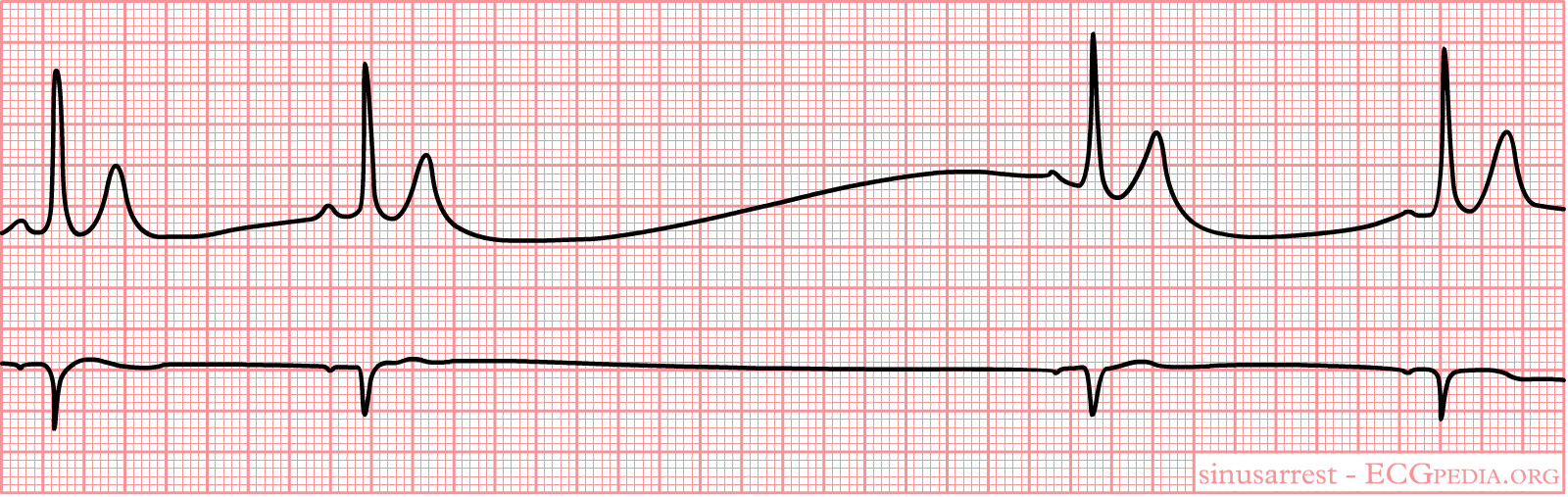
Normal sinus rhythm wikidoc
Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic.
See A Sample Ekg Rhythm.
Learn how to identify and interpret sinoatrial arrest and pause on ecg, which occur when the sinoatrial node fails to discharge an impulse for ≥2. Learn how to identify sinus arrest, a pause in the electrical activity initiated by the sa node, on the ekg. Learn how to identify and interpret sinus pause or sinus arrest on the ecg, a type of dysrhythmia that can cause fainting or require. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;.