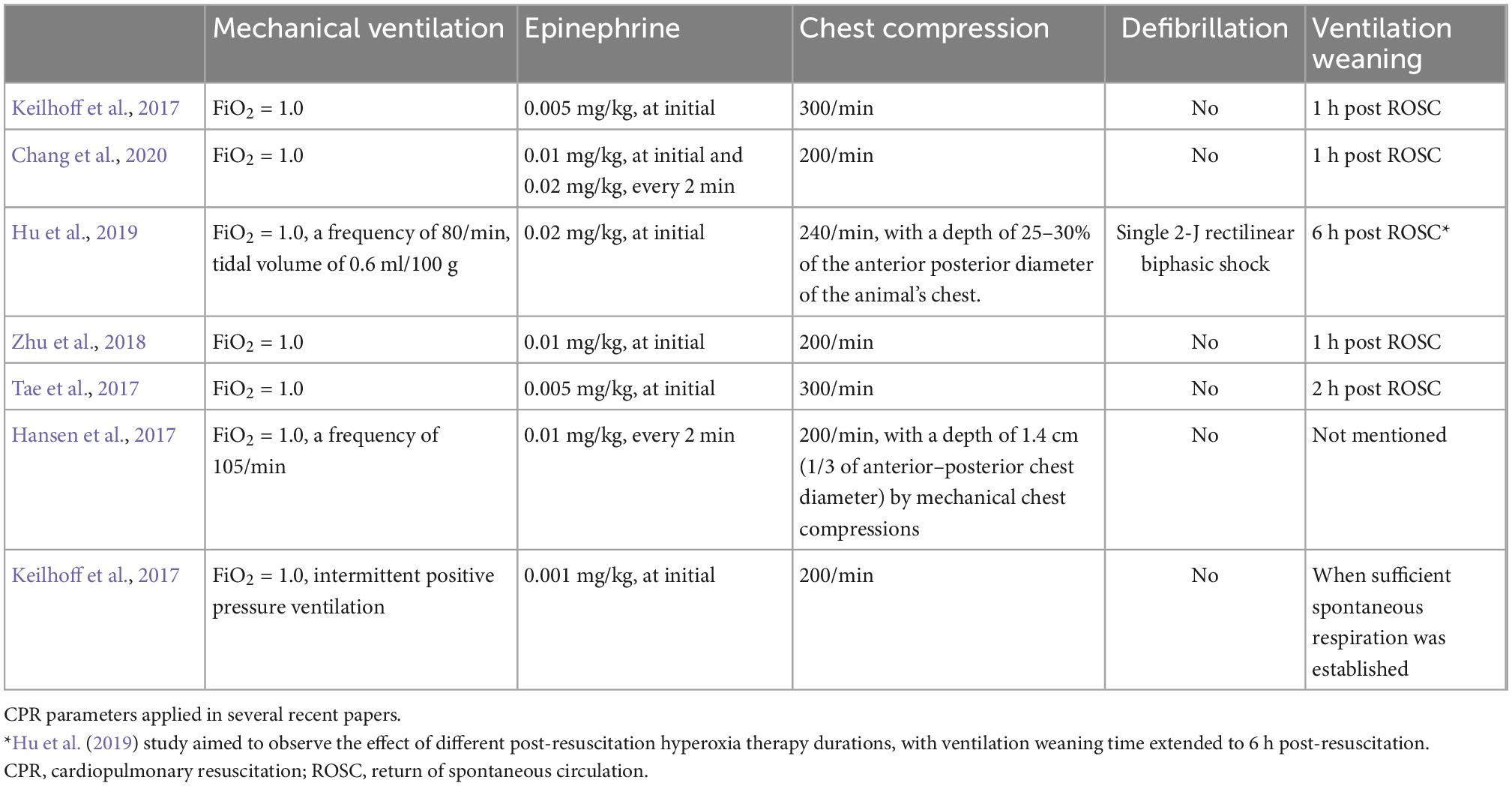
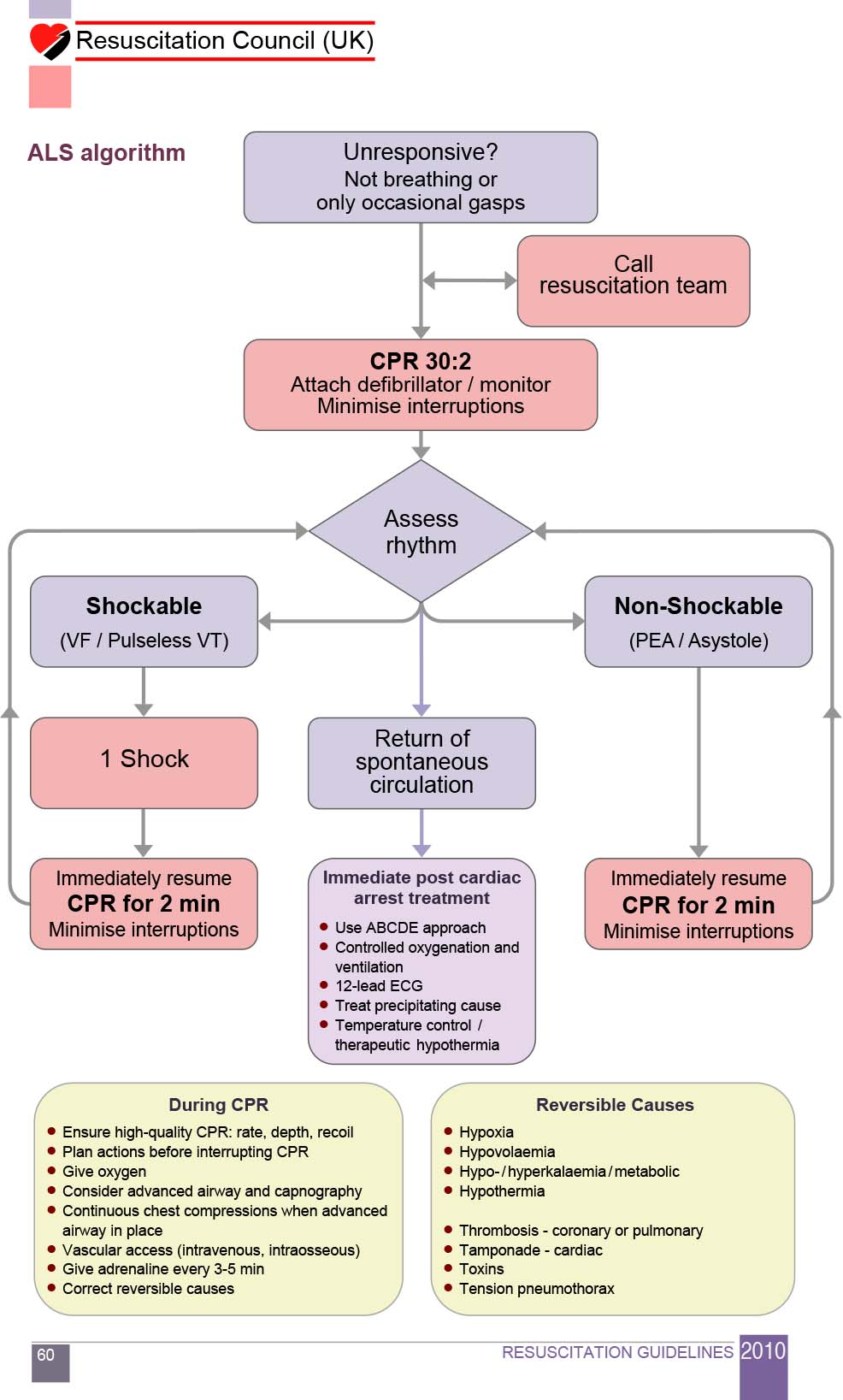
What Is Critical In Reducing Pediatric Cardiac Arrest From Asphyxia
What Is Critical In Reducing Pediatric Cardiac Arrest From Asphyxia - This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart. Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest.
May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest. Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart. Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and.
May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart. Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric.
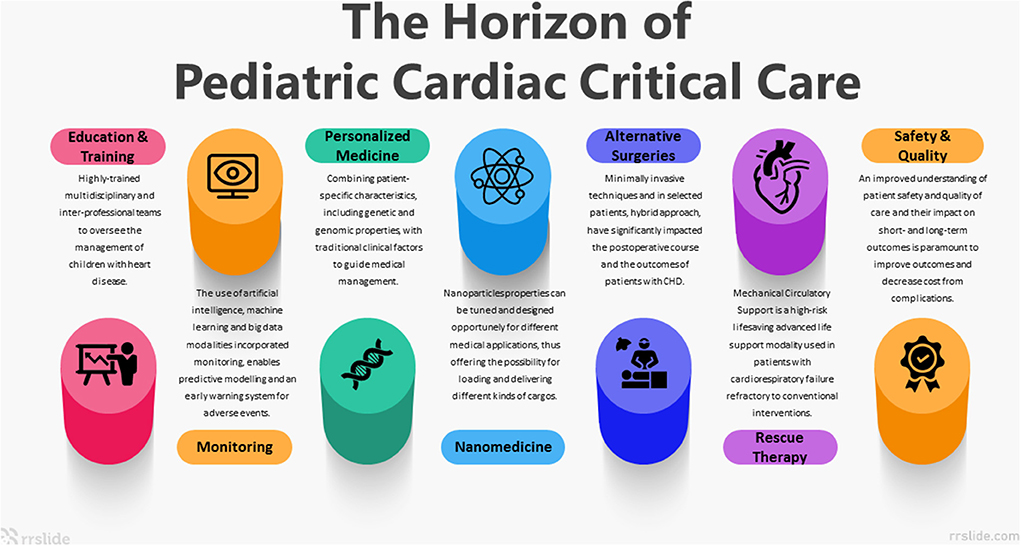
Frontiers The horizon of pediatric cardiac critical care
Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest. Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart. May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: This update provides the evidence.
Part 4 Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support American Heart
This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. Hospitals around the country collaborate to.
PALS Certification Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. Hospitals around the country collaborate to.
Part 13 Pediatric Basic Life Support Circulation
Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest..
Part 11 Pediatric Basic Life Support and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest..
Pediatric PostCardiac Arrest Care A Scientific Statement From the
This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by.
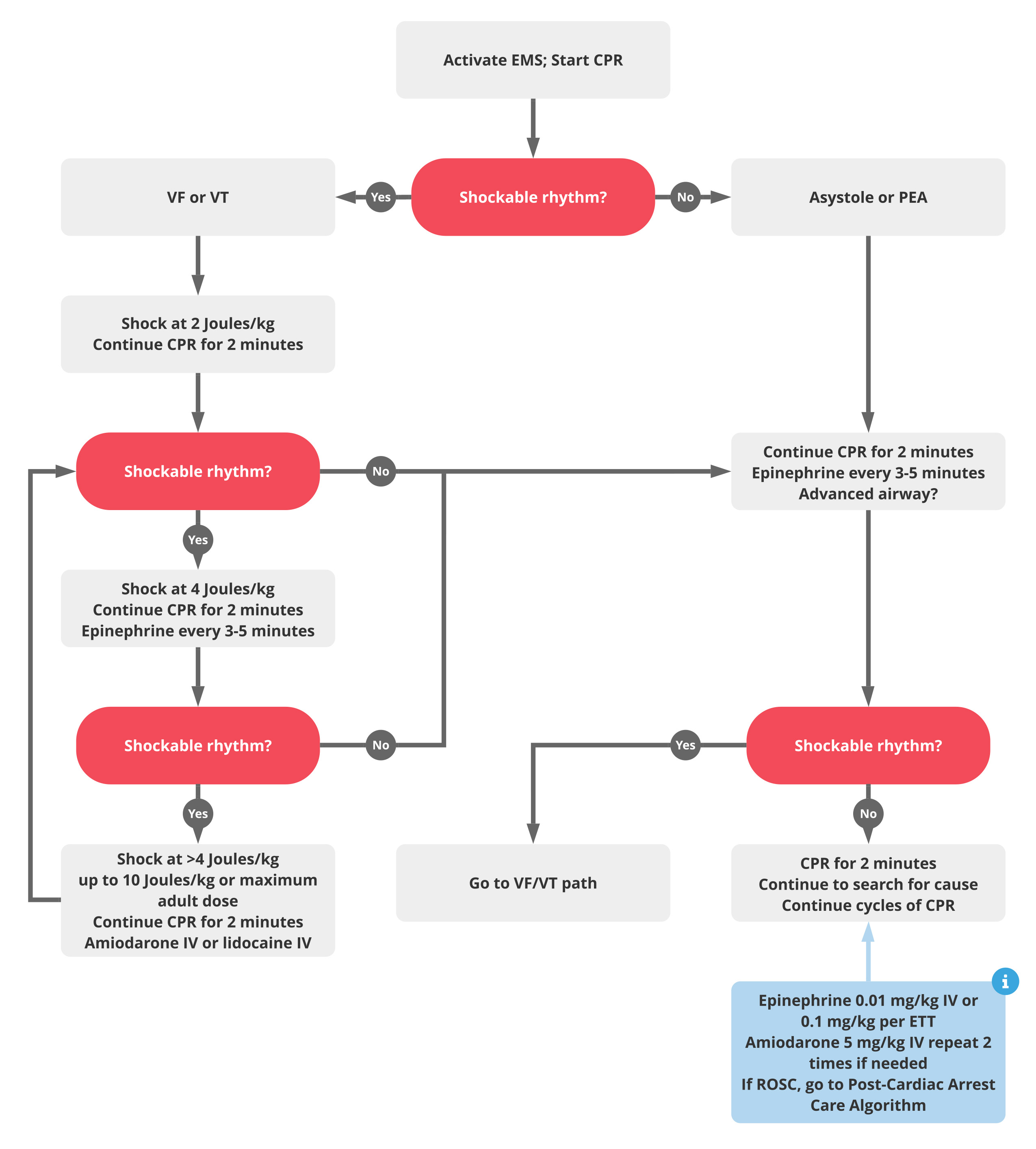
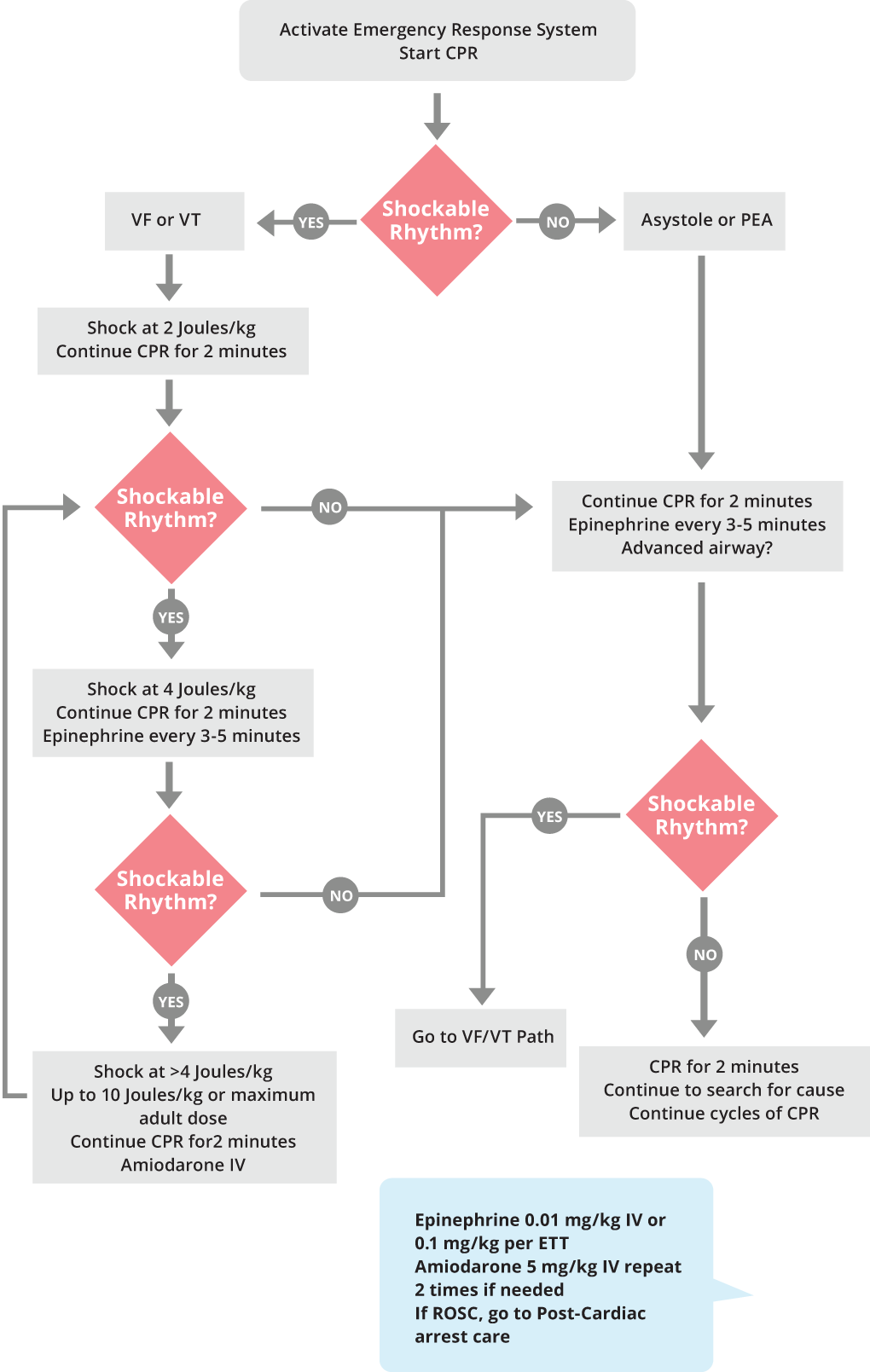
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Sequence ACLS Medical Training
Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart. Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest. May repeat.
Frontiers Rat model of asphyxiainduced cardiac arrest and resuscitation
This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest. Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart. Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. May repeat up to 3.
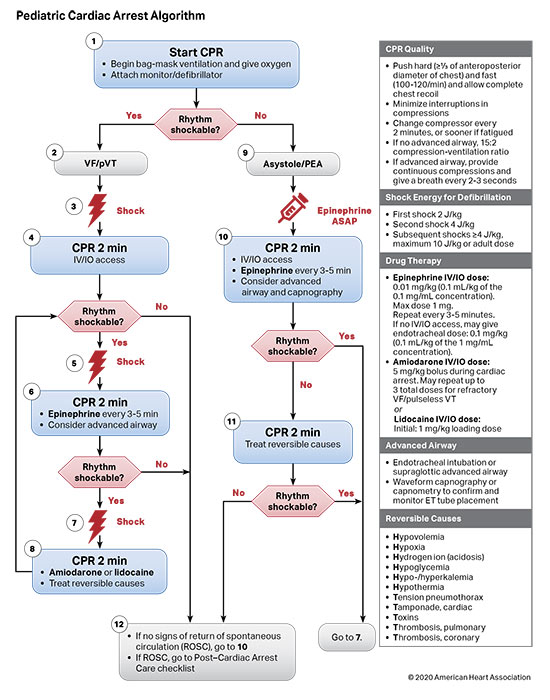
Algorithms Paediatric Cardiac Arrest Management
Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to ischaemic injury but may exhibit increased neuroplasticity. This update provides the evidence review and treatment recommendations for advanced airway management in pediatric. May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest. Hospitals around the country collaborate to.
Cardiac Arrest Oxford Medical Education
Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart. Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: Firstly, the developing brain is likely to be more sensitive to.
This Update Provides The Evidence Review And Treatment Recommendations For Advanced Airway Management In Pediatric.
5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac arrest. Pediatric cardiopulmonary arrest is a unique entity, distinct from adult cardiac arrest (ca) in etiology, early pathophysiology and. Cardiac arrest in children is most often caused by progressive asphyxia from acute hypoxia or hypercarbia, which leads to acidosis and. Hospitals around the country collaborate to significantly reduce cardiac arrest rates among children hospitalized with heart.
Firstly, The Developing Brain Is Likely To Be More Sensitive To Ischaemic Injury But May Exhibit Increased Neuroplasticity.
May repeat up to 3 total doses for refractory vf/pulseless vt or lidocaine iv/io dose: